Working Principal, Explanation with Diagram, Solved Example Problems - Van de Graaff Generator | 12th Physics : Electrostatics
Chapter: 12th Physics : Electrostatics
Van de Graaff Generator
Van de Graaff Generator
In the year 1929, Robert
Van de Graaff designed a machine which produces a large amount of electrostatic
potential difference, up to several million volts (107 V). This Van
de Graff generator works on the principle of electrostatic induction and action
at points.
A large hollow spherical
conductor is fixed on the insulating stand as shown in Figure 1.65. A pulley B
is mounted at the center of the hollow sphere and another pulley C is fixed at
the bottom. A belt made up of insulating materials like silk or rubber runs
over both pulleys. The pulley C is driven continuously by the electric motor.
Two comb shaped metallic conductors E and D are fixed near the pulleys.
The comb D is maintained
at a positive potential of 104 V by a power supply. The upper comb E
is connected to the inner side of the hollow metal sphere.
Due to the high electric field near comb D, air between the belt and comb D gets ionized. The positive charges are pushed towards the belt and negative charges are attracted towards the comb D. The positive charges stick to the belt and move up.
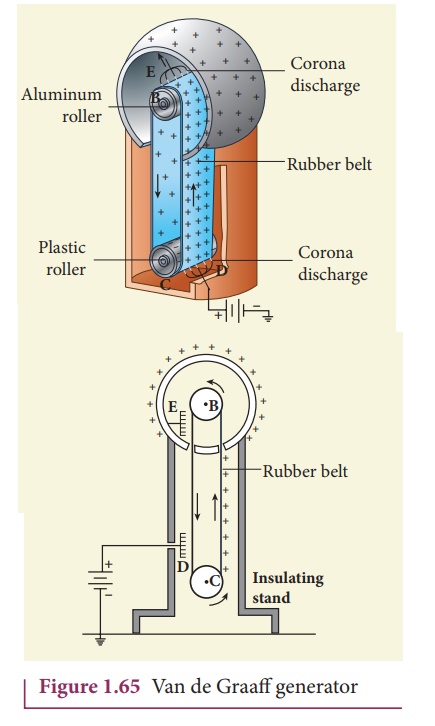
When the positive charges reach the comb E, a large amount
of negative and positive charges are induced on either side of comb E due to
electrostatic induction. As a result, the positive charges are pushed away from
the comb E and they reach the outer surface of the sphere. Since the sphere is
a conductor, the positive charges are distributed uniformly on the outer
surface of the hollow sphere. At the same time, the negative charges nullify
the positive charges in the belt due to corona discharge before it passes over
the pulley.
When the belt descends,
it has almost no net charge. At the bottom, it again gains a large positive
charge. The belt goes up and delivers the positive charges to the outer surface
of the sphere. This process continues until the outer surface produces the
potential difference of the order of 107 which is the limiting value. We cannot
store charges beyond this limit since the extra charge starts leaking to the
surroundings due to ionization of air. The leakage of charges can be reduced by
enclosing the machine in a gas filled steel chamber at very high pressure.
The high voltage
produced in this Van de Graaff generator is used to accelerate positive ions
(protons and deuterons) for nuclear disintegrations and other applications.
EXAMPLE 1.24
Dielectric strength of
air is 3 × 106 V m-1. Suppose the radius of a hollow
sphere in the Van de Graff generator is R = 0.5 m, calculate the maximum
potential difference created by this Van de Graaff generator.
The electric field on
the surface of the sphere (by Gauss law) is given by
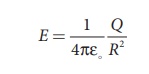
The potential on the
surface of the hollow metallic sphere is given by
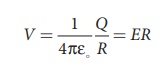
with Vmax = EmaxR
Here Emax = 3
×106 V/m . So the maximum potential difference created is given by
Vmax = 3 × 106
× 0.5
= 1.5 × 106 V
(or) 1.5 million volt
Related Topics