Electrostatics of Conductors and Dielectrics - Dielectrics or insulators | 12th Physics : Electrostatics
Chapter: 12th Physics : Electrostatics
Dielectrics or insulators
Dielectrics or insulators
A dielectric is a
non-conducting material and has no free electrons. The electrons in a
dielectric are bound within the atoms. Ebonite, glass and mica are some
examples of dielectrics. When an external electric field is applied, the
electrons are not free to move anywhere but they are realigned in a specific
way. A dielectric is made up of either polar molecules or non-polar molecules.
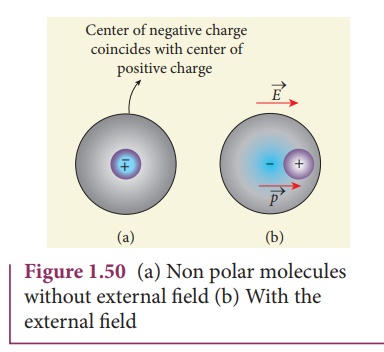
Non-polar molecules
A non-polar molecule is
one in which centers of positive and negative charges coincide. As a result, it
has no permanent dipole moment. Examples of non-polar molecules are hydrogen (H2),
oxygen (O2), and carbon dioxide (CO2) etc.
When an external
electric field is applied, the centers of positive and negative charges are separated
by a small distance which induces dipole moment in the direction of the
external electric field. Then the dielectric is said to be polarized by an
external electric field. This is shown in Figure 1.50.
Polar molecules
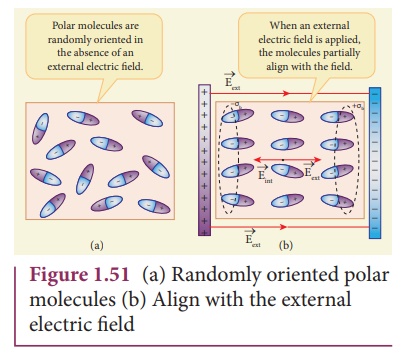
In polar molecules, the
centers of the positive and negative charges are separated even in the absence
of an external electric field. They have a permanent dipole moment. Due to
thermal motion, the direction of each dipole moment is oriented randomly
(Figure 1.51(a)). Hence the net dipole moment is zero in the absence of an
external electric field. Examples of polar molecules are H2O,
N2O, HCl, NH3.
When an external
electric field is applied, the dipoles inside the polar molecule tend to align
in the direction of the electric field. Hence a net dipole moment is induced in
it. Then the dielectric is said to be polarized by an external electric field
(Figure 1.51(b)).
Polarisation
In the presence of an
external electric field, the dipole moment is induced in the dielectric
material. Polarisation P is defined as the total
dipole moment per unit volume of the dielectric. For most dielectrics
(linear isotropic), the Polarisation is directly proportional to the strength
of the external electric field. This is written as

where Ōáe is a constant called
the electric susceptibility which is a characteristic of each dielectric.
Related Topics