Electrostatics - Historical background of electric charges | 12th Physics : Electrostatics
Chapter: 12th Physics : Electrostatics
Historical background of electric charges
Historical background of electric charges
Two millenniums ago,
Greeks noticed that amber (a solid, translucent material formed from the resin
of a fossilized tree) after rubbing with animal fur attracted small pieces of
leaves and dust. The amber possessing this property is said to be ‘charged’. It
was initially thought that amber has this special property. Later people found
that not only amber but even a glass rod rubbed with silk cloth, attracts
pieces of papers. So glass rod also becomes ‘charged’ when rubbed with a
suitable material.![]()
![]()
Consider a charged
rubber rod hanging from a thread as shown in Figure 1.1. Suppose another
charged rubber rod is brought near the first rubber rod; the rods repel each
other. Now if we bring a charged glass rod close to the charged rubber rod,
they attract each other. At the same time, if a charged glass rod is brought
near another charged glass rod, both the rods repel each other.
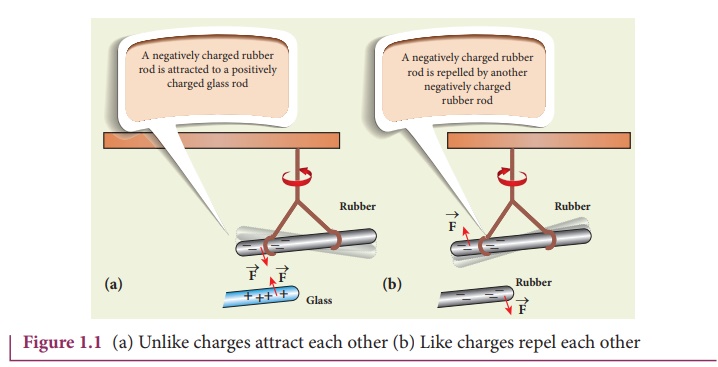
From these observations,
the following inferences are made
i.
The charging of rubber rod and that of glass rod are different
from one another.
ii.
The charged rubber rod repels another charged rubber rod, which
implies that ‘like charges repel each other’. We can also arrive at the same
inference by observing that a charged glass rod repels another charged glass
rod.
iii.
The charged amber rod attracts the charged glass rod, implying
that the charge in the glass rod is not the same kind of charge present
in the rubber.
Thus unlike charges attract each other. Therefore, two kinds of charges exist in the universe. In the 18th century, Benjamin Franklin called one type of charge as positive (+) and another type of charge as negative (-). Based on Franklin’s convention, rubber and amber rods are negatively charged while the glass rod is positively charged. If the net charge is zero in the object, it is said to be electrically neutral.
Following the pioneering
work of J. J. Thomson and E. Rutherford, in the late 19th century and in the
beginning of 20th century, we now understand that the atom is electrically
neutral and is made up of the negatively charged electrons, positively charged
protons, and neutrons which have zero charge. The material objects made up of atoms
are neutral in general. When an object is rubbed with another object (for
example rubber with silk cloth), some amount of charge is transferred from one
object to another due to the friction between them and the object is then said
to be electrically charged. Charging the objects through rubbing is
called triboelectric charging.
Related Topics