Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 8 : Heat and Thermodynamics
Thermal expansion of solids, liquids and gases
Thermal
expansion of solids, liquids and gases
Thermal expansion is the tendency of
matter to change in shape, area, and volume due to a change in temperature.
All
three states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) expand when heated. When a solid
is heated, its atoms vibrate with higher amplitude about their fixed points.
The relative change in the size of solids is small. Railway tracks are given
small gaps so that in the summer, the tracks expand and do not buckle. Railroad
tracks and bridges have expansion joints to allow them to expand and contract
freely with temperature changes. It is shown in Figure 8.3

Liquids, have less intermolecular forces than solids and hence they expand more
than solids. This is the principle behind the mercury thermometers.
![]()
![]() In the case of gas
molecules, the intermolecular forces are almost negligible and hence they
expand much more than solids. For example in hot air balloons when gas
particles get heated, they expand and take up more space.
In the case of gas
molecules, the intermolecular forces are almost negligible and hence they
expand much more than solids. For example in hot air balloons when gas
particles get heated, they expand and take up more space.
The
increase in dimension of a body due to the increase in its temperature is called
thermal expansion.
The expansion in length is called linear expansion. Similarly the expansion in area is termed as area expansion and the expansion in volume is termed as volume expansion. It is shown in Figure 8.4
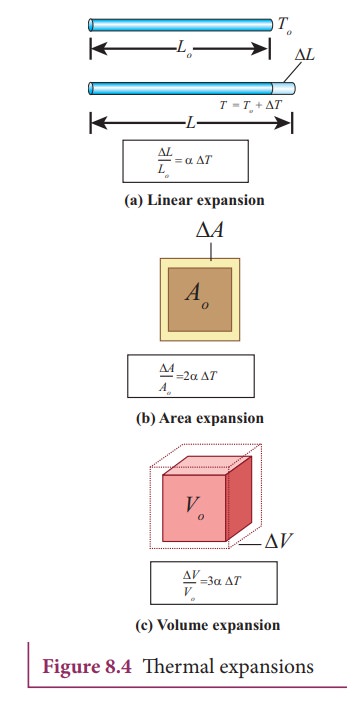
Linear Expansion
In
solids, for a small change in temperature ╬öT, the fractional change in length (ŌłåL/L)
is directly proportional to ΔT.
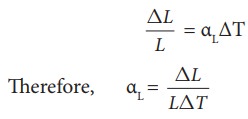
Where,
╬▒L = coefficient of linear expansion.
ΔL
= Change in length
L
= Original length
ΔT = Change in temperature.
EXAMPLE 8.6
Eiffel
tower is made up of iron and its height is roughly 300 m. During winter season
(January) in France the temperature is 2┬░C and in hot summer its average
temperature 25┬░C. Calculate the change in height of Eiffel tower between summer
and winter. The linear thermal expansion coefficient for iron ╬▒ = 10 ├Ś10ŌłÆ6 per ┬░C

Solution
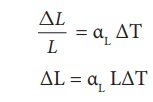
ΔL
= 10 ├Ś 10ŌłÆ6 ├Ś
300 ├Ś 23 = 0.69 m=69 cm
Area Expansion
For
a small change in temperature ╬öT the fractional change in area (ŌłåA/A) of a
substance is directly proportional to ΔT and it can be written as
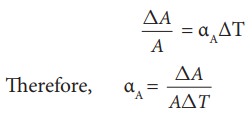
Where,
╬▒A
= coefficient of area expansion.
ΔA
= Change in area
A
= Original area
ΔT
= Change in temperature
Volume Expansion
For
a small change in temperature ΔT the fractional change in volume (ΔV/V) of a
substance is directly proportional to ΔT.
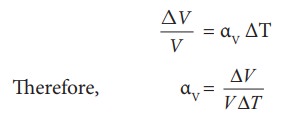
Where, ╬▒V = coefficient of volume expansion.
ΔV
= Change in volume
V
= Original volume
ΔT
= Change in temperature
Unit
of coefficient of linear, area and volumetric expansion of solids is ˚C-1
or K-1
Related Topics