Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 8 : Heat and Thermodynamics
Heat transfer
Heat
transfer
As
we have seen already heat is a energy in transit which is transferred from one
body to another body due to temperature difference. There are three modes of heat
transfer: Conduction, Convection and Radiation.
Conduction
Conduction
is the process of direct transfer of heat through matter due to temperature
difference. When two objects are in direct contact with one another, heat will
be transferred from the hotter object to the colder one. The objects which
allow heat to travel easily through them are called conductors.
Thermal conductivity
Thermal
conductivity is the ability to conduct heat.
The quantity of heat transferred
through a unit length of a material in a direction normal to unit surface area
due to a unit temperature difference under steady state conditions is known as
thermal conductivity of a material.
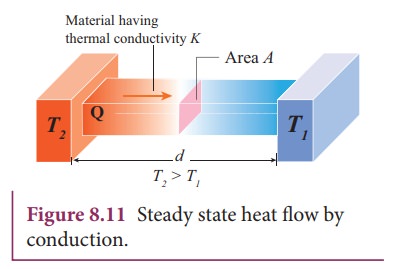
In
steady state, the rate of flow of heat Q is proportional to the temperature
difference ΔT and the area of cross section A and is inversely proportional to
the length L. So the rate of flow of heat is written as
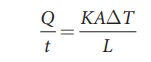
Where,
K is known as the coefficient of thermal conductivity.
(Not
to be confused with Kelvin represented by upper case K)
The
SI unit of thermal conductivity is J s-1 m-1 K-1
or W m-1 K-1.
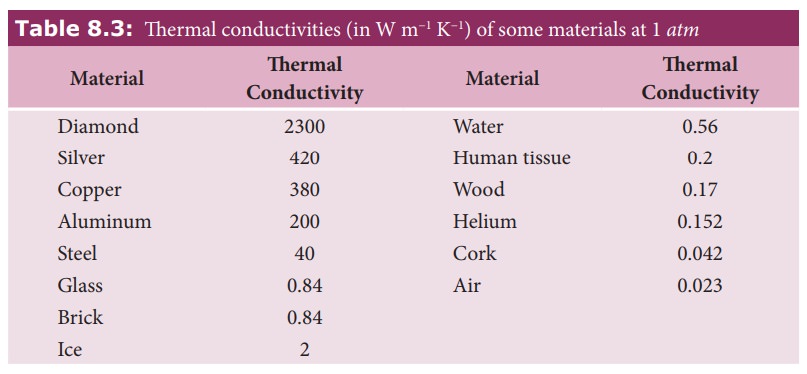
Thermal conductivity depends on the nature of the material. For example silver and aluminum have high thermal conductivities. So they are used to make cooking vessels.
Convection
Convection is the process in which heat transfer is by actual movement of molecules in fluids such as liquids and gases. In convection, molecules move freely from one place to another. It happens naturally or forcefully.
Boiling water in a cooking pot is an example of convection.
Water at the bottom of the pot receives more heat. Due to heating, the water
expands and the density of water decreases at the bottom. Due to this decrease
in density, molecules rise to the top. At the same time the molecules at the
top receive less heat and become denser and come to the bottom of the pot. This
process goes on continuously. The back and forth movement of molecules is
called convection current.
To
keep the room warm, we use room heater. The air molecules near the heater will
heat up and expand. As they expand, the density of air molecules will decrease
and rise up while the higher density cold air will come down. This circulation
of air molecules is called convection current.
Radiation:
When
we keep our hands near the hot stove we feel the heat even though our hands are
not touching the hot stove. Here heat transferred from the hot stove to our
hands is in the form of radiation. We receive energy from the sun in the form
of radiations. These radiations travel through vacuum and reach the Earth. It
is the peculiar character of radiation which requires no medium to transfer
energy from one object to another. The conduction or convection requires medium
to transfer the heat.
Radiation
is a form of energy transfer from one body to another by electromagnetic waves.
Example:
1.
Solar energy from the Sun.
2.
Radiation from room heater.
Related Topics