Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 8 : Heat and Thermodynamics
Specific Heat Capacity of a Gas
SPECIFIC
HEAT CAPACITY OF A GAS
Specific
heat capacity of a given system plays a very important role in determining the
structure and molecular nature of the system. Unlike solids and liquids, gases
have two specific heats: specific heat capacity at constant pressure (sp) and specific heat
capacity at constant volume (sv).
Specific heat capacity
Specific heat capacity at constant
pressure (sp):
The
amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one kg of a
substance by 1 K or 1┬░C by keeping the pressure constant is called specific
heat capacity of at constant pressure. When the heat energy is supplied to the
gas, it expands to keep the pressure constant as shown in Figure 8.23
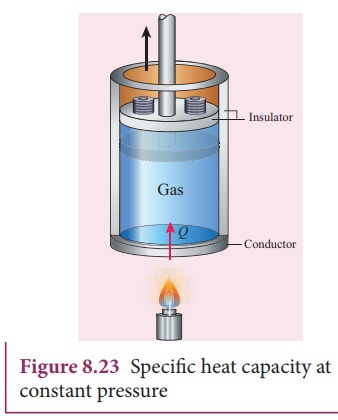
In
this process a part of the heat energy is used for doing work (expansion) and
the remaining part is used to increase the internal energy of the gas.
Specific heat capacity at constant volume (sv):
The
amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one kg of a
substance by 1 K or 1┬░C by keeping the volume constant is called specific heat
capacity at constant volume.
![]()
![]() If the volume is kept constant, then the supplied heat is
used to increase only the internal energy. No work is done by the gas as shown
in Figure 8.24.
If the volume is kept constant, then the supplied heat is
used to increase only the internal energy. No work is done by the gas as shown
in Figure 8.24.
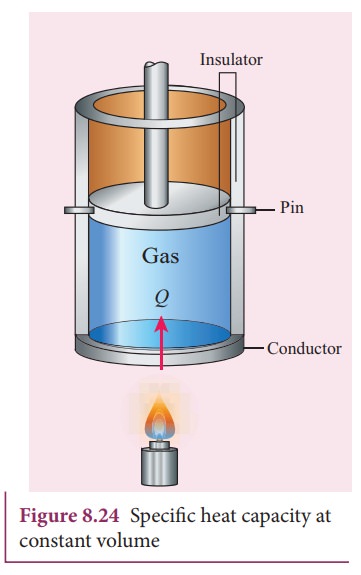
It
implies that to increase the temperature of the gas at constant volume requires
less heat than increasing the temperature of the gas at constant pressure. In
other words sp is always greater than sv.
Molar Specific heat capacities
Sometimes
it is useful to calculate the molar heat capacities Cp and Cv.
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance
by 1K or 1┬░C at constant volume is called molar specific heat capacity at
constant volume (Cv). If pressure is kept constant, it is called
molar specific heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp).
If
Q is the heat supplied to mole of a gas at constant volume and if the
temperature changes by an amount DT
, we have

By
applying the first law of thermodynamics for this constant volume process (W=0,
since dV=0), we have

By
comparing the equations (8.18) and (8.19),
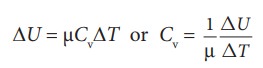
If
the limit DT goes to zero, we can write

Since
the temperature and internal energy are state variables, the above relation
holds true for any process.
MeyerŌĆÖs relation
Consider
┬Ą mole of an ideal gas in a container with volume V, pressure P and temperature
T.
When
the gas is heated at constant volume the temperature increases by dT. As no
work is done by the gas, the heat that flows into the system will increase only
the internal energy. Let the change in internal energy be dU.
If
Cv is the molar specific heat capacity at constant volume, from
equation (8.20)

Suppose
the gas is heated at constant pressure so that the temperature increases by dT.
If ŌĆśQŌĆÖ is the heat supplied in this process and ŌĆśdVŌĆÖ the change in volume of
the gas.

If
W is the workdone by the gas in this process, then

But
from the first law of thermodynamics,

Substituting
equations (8.21), (8.22) and (8.23) in (8.24), we get,
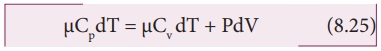
For
mole of ideal gas, the equation of state is given by
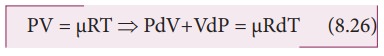
Since
the pressure is constant, dP=0
Ōł┤CpdT = CvdT +RdT
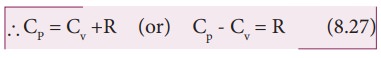
This
relation is called MeyerŌĆÖs relation
It
implies that the molar specific heat capacity of an ideal gas at constant
pressure is greater than molar specific heat capacity at constant volume.
The
relation shows that specific heat at constant pressure (sp) is
always greater that specific heat at constant volume (sv).
Related Topics