Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Solved Example Problems on Alternating Current (AC) and Circuit
RMS value of AC:
EXAMPLE 4.18
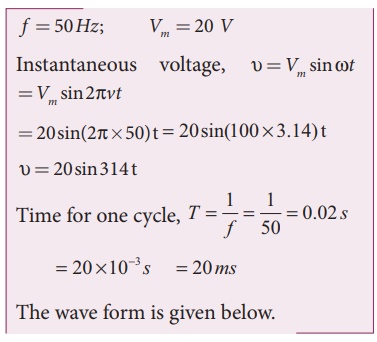
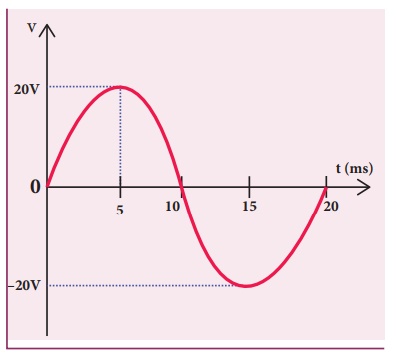
Write down the equation for a sinusoidal voltage of 50 Hz and its peak value is 20 V. Draw the corresponding voltage versus time graph.
Solution
EXAMPLE 4.19
The equation for an alternating current is given by i = 77 sin 314t. Find the peak value, frequency, time period and instantaneous value at t = 2 ms.
Solution
i = 77 sin 314t ; t = 2 ms = 2├Ś10-3 s
The general equation of an alternating current is i = Im sin Žēt . On comparsion,
(i) Peak value, Im = 77 A
(ii) Frequency, f = Žē/2ŽĆ = 314 / 2 ├Ś3.14 = 50 Hz
Time period, T = 1/f = 150 = 0 .02 s
(iv) At t = 2 m s,
Instantaneous value,
i = 77sin(314├Ś2├Ś10ŌłÆ3 )
i = 45.24 A
AC circuit containing only an inductor: Solved Example Problems
EXAMPLE 4.20
A 400 mH coil of negligible resistance is connected to an AC circuit in which an effective current of 6 mA is flowing. Find out the voltage across the coil if the frequency is 1000 Hz.
Solution
L = 400 x 10-3 H; Ieff = 6 x 10-3A
f = 1000 Hz

AC circuit containing only a capacitor: Solved Example Problems
EXAMPLE 4.21
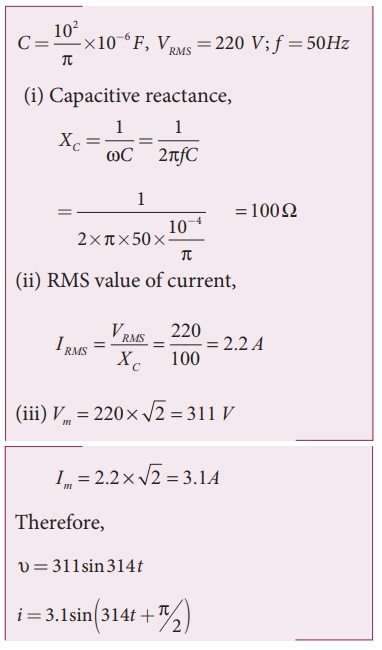
A capacitor of capacitance 102/ŽĆ ┬ĄF is connected across a 220 V, 50 Hz A.C. mains. Calculate the capacitive reactance, RMS value of current and write down the equations of voltage and current.
Solution
Quality factor or QŌĆōfactor: Solved Example Problems
EXAMPLE 4.22
Find the impedance of a series RLC circuit if the inductive reactance, capacitive reactance and resistance are 184 ╬®, 144 ╬® and 30 ╬® respectively. Also calculate the phase angle between voltage and current.
Solution
XL = 184 ╬®; XC = 144 ╬®
R = 30 ╬®
(i ) The impedance is
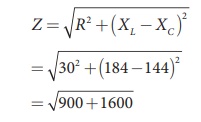
Impedance, Z = 50 Ōä”
(ii) Phase angle is
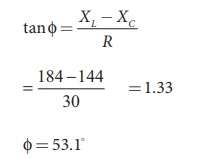
Žå = 53.1
EXAMPLE 4.23
A 500 ╬╝H inductor, 80/ŽĆ2 pF capacitor and a 628 ╬® resistor are connected to form a series RLC circuit. Calculate the resonant frequency and Q-factor of this circuit at resonance.
Solution
L=500├Ś10-6H; C = 80/ŽĆ2 ├Ś10ŌłÆ12 F; R = 628Ōä”
(i) Resonant frequency is
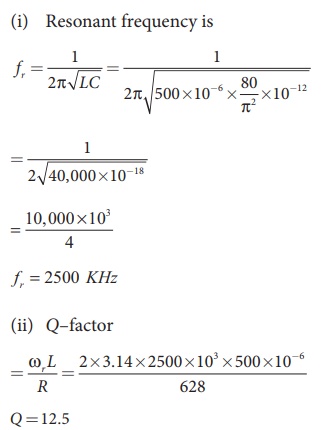
Q =12.5
EXAMPLE 4.24
Find the instantaneous value of alternating voltage Žģ = 10 sin(3 ŽĆ├Ś104 t) volt at i) 0ŌĆås ii) 50 ╬╝s iii) 75 ╬╝s.
Solution
The given equation is Žģ = 10sin (3 ŽĆ├Ś104 t)

EXAMPLE 4.25
The current in an inductive circuit is given by 0.3 sin (200t ŌĆō 40┬░) A. Write the equation for the voltage across it if the inductance is 40 mH.
Solution
L = 40 ├Ś 10-3 H; i = 0.1 sin (200t ŌĆō 40┬║)
XL = ŽēL = 200 ├Ś 40 ├Ś 10-3 = 8 Ōä”
Vm = Im XL = 0.3 ├Ś 8 = 2.4 V
In an inductive circuit, the voltage leads the current by 90o Therefore,
v = Vm sin ( Žēt +90┬║)
v = 2 . 4 sin(200t ŌłÆ40 + 90 ┬║)
v = 2 . 4 sin(200t +50 ┬║)volt
Related Topics