Phasor diagram, Circuit Diagram, Formula, Solved Example Problems | Alternating Current (AC) - AC circuit containing only a capacitor | 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
AC circuit containing only a capacitor
AC circuit containing only a capacitor
Consider a circuit
containing a capacitor of capacitance C connected across an alternating
voltage source (Figure 4.49). The alternating voltage is given by
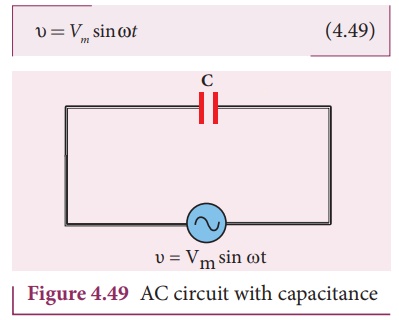
Let q be the
instantaneous charge on the capacitor. The emf across the capacitor at that
instant is q/C According to Kirchoff’s loop rule,
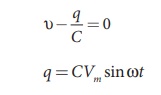
By the definition of
current,
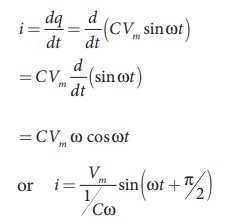
Instantaneous value of
current,

where [Vm] /
[1/Cω] = Im , the peak value of the alternating current. From equations (4.49) and
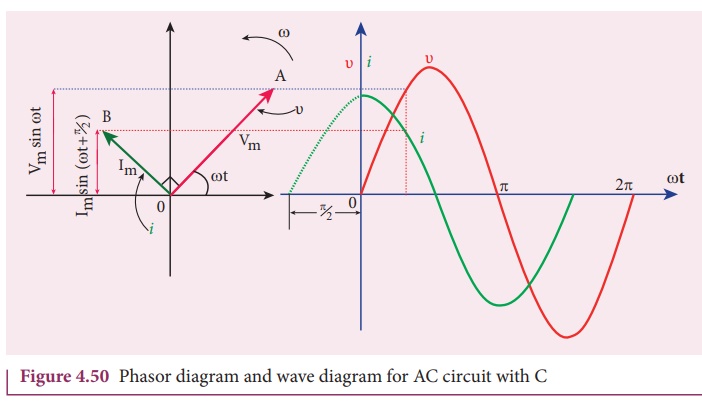
(4.50), it is clear that current leads the applied voltage by π/2 in a
capacitive circuit. This is shown pictorially in Figure 4.50. The wave diagram
for a capacitive circuit also shows that the current leads the applied voltage
by 90Âş.
Capacitive reactance XC
The peak value of
current Im is given by Im = [Vm] /
[1/Cω]. . Let us compare this equation
with Im = Vm/R from resistive circuit. The quantity 1/ Cω plays the same role as the resistance R in
resistive circuit. This is the resistance offered by the capacitor, called capacitive reactance (XC).
It measured in ohm.

The capacitive reactance
(XC) varies inversely as the frequency. For a steady current,
f = 0.
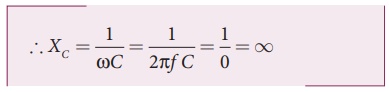
Thus a capacitive
circuit offers infinite resistance to the steady current. So that steady
current cannot flow through the capacitor.
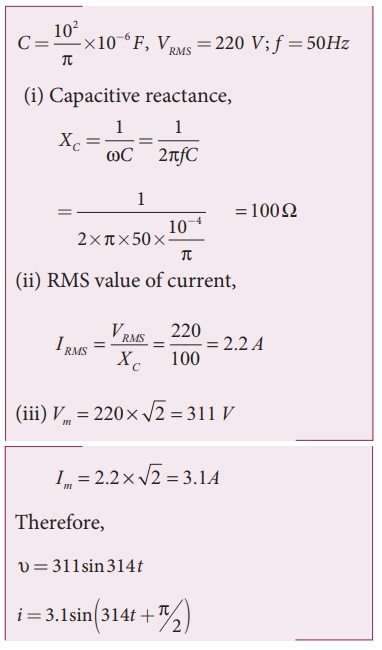
EXAMPLE 4.21
A capacitor of
capacitance 102/π µF is connected across a 220 V, 50 Hz A.C. mains.
Calculate the capacitive reactance, RMS value of current and write down the
equations of voltage and current.
Solution
Related Topics