Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Illustration and Solved Example Problems on Advantages of AC in long distance power transmission
Illustration:
An electric power of 2 MW is transmitted to a place through transmission lines of total resistance, say R = 40 Ω, at two different voltages. One is lower voltage (10 kV) and the other is higher (100 kV). Let us now calculate and compare power losses in these two cases.
Case (i):
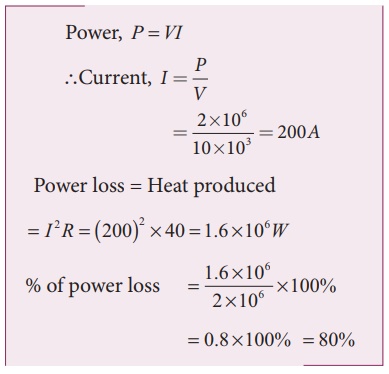
P = 2 MW; R = 40 Ω; V = 10 kV
Case (ii):
P = 2 MW; R = 40 Ω; V = 100 kV
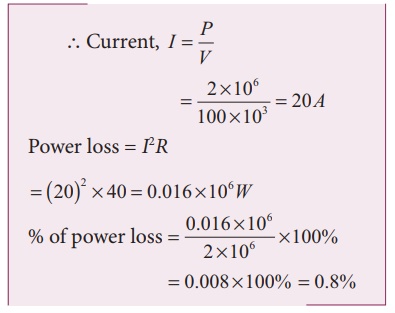
Thus it is clear that when an electric power is transmitted at higher voltage, the power loss is reduced to a large extent.
EXAMPLE 4.16
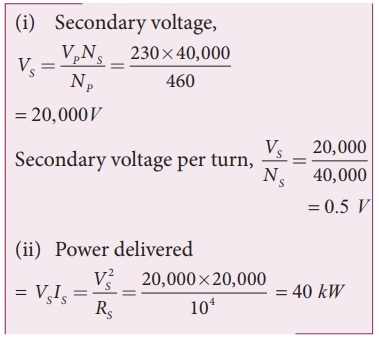
An ideal transformer has 460 and 40,000 turns in the primary and secondary coils respectively. Find the voltage developed per turn of the secondary if the transformer is connected to a 230 V AC mains. The secondaryisgiventoaloadofresistance104Ω. Calculate the power delivered to the load.
Solution
NP = 460 turns; NS = 40,000 turns
VP = 230 V; RS = 104 Ω
EXAMPLE 4.17
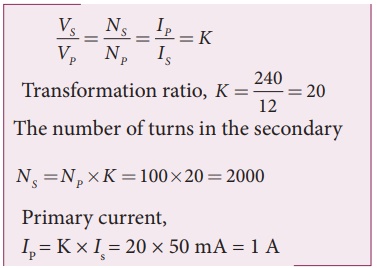
An inverter is common electrical device which we use in our homes. When there is no power in our house, inverter gives AC power to run a few electronic appliances like fan or light. An inverter has inbuilt step-up transformer which converts 12 V AC to 240 V AC. The primary coil has 100 turns and the inverter delivers 50 mA to the external circuit. Find the number of turns in the secondary and the primary current.
Solution
Vp = 12 V; Vs = 240 V
Is = 50mA; Np = 100 turns
Related Topics