Introduction, Definition, Formula - Alternating Current (AC) | 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Alternating Current (AC)
ALTERNATING CURRENT
Introduction
In section (AC GENERATOR),
we have seen that when the orientation of the coil with the magnetic field is
changed, an alternating emf is induced and hence an alternating current flows
in the closed circuit. An alternating voltage is the voltage which
changes polarity at regular intervals of time and the direction of the
resulting alternating current also changes accordingly.
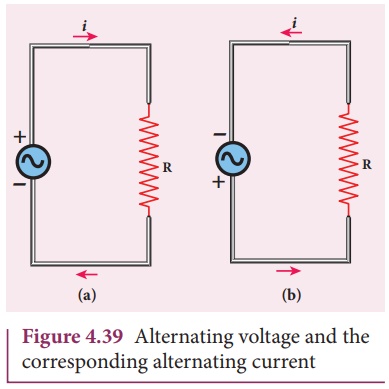
In the Figure 4.39(a),
an alternating voltage source is connected to a resistor R in which the
upper terminal of the source is positive and lower terminal negative at an
instant. Therefore, the current flows in clockwise direction. After a short
time, the polarities of the source are reversed so that current now flows in
anti-clockwise direction (Figure 4.39(b)). This current which flows in
alternate directions in the circuit is called alternating current.
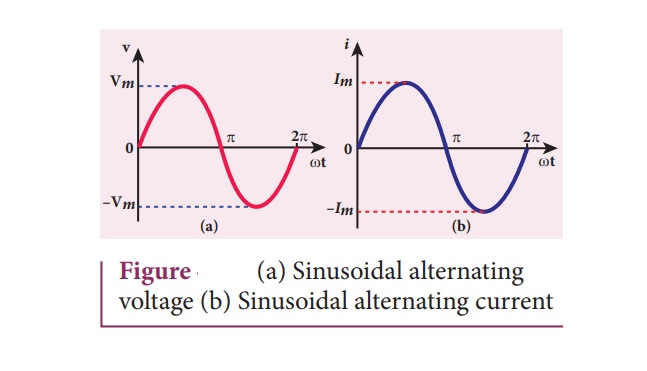
Sinusoidal alternating
voltage
If the waveform of
alternating voltage is a sine wave, then it is known as sinusoidal alternating
voltage which
is given by the relation.

where Ď… is the
instantaneous value of alternating voltage; Vm is the maximum
value (amplitude) and ω is the angular frequency of the alternating voltage.
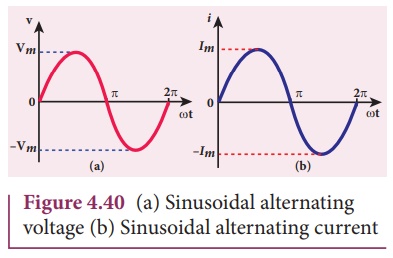
When sinusoidal alternating voltage is applied to a closed circuit, the
resulting alternating current is also sinusoidal in nature and its relation is

where Im
is the maximum value (amplitude) of the alternating current. The direction of
sinusoidal voltage or current is reversed after every half-cycle and its
magnitude is also changing continuously as shown in Figure 4.40.
Related Topics