Definition, Formula, Solved Example Problems | Electromagnetic Induction - Magnetic Flux | 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Magnetic Flux
Magnetic Flux (ΦB)
The magnetic flux
through an area A in a magnetic field is defined as the number of
magnetic field lines passing through that area normally and is given by the
equation (Figure 4.1(a)).

where the integral is
taken over the area A and θ is the angle between the direction of
the magnetic field and the outward normal to the area.
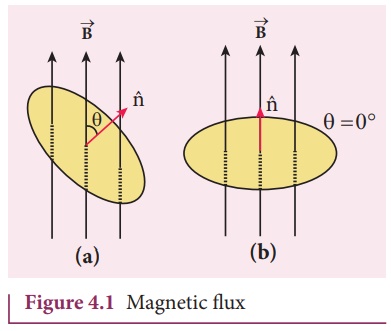
If the magnetic field ![]() is uniform over the area A and is perpendicular to the area as shown in
Figure 4.1(b), then the above equation becomes
is uniform over the area A and is perpendicular to the area as shown in
Figure 4.1(b), then the above equation becomes

The SI unit of magnetic
flux is T m2. It is also measured in weber or Wb.
1 Wb = 1 T m2
EXAMPLE 4.1
A circular antenna of
area 3 m2 is installed at a place in Madurai. The plane of the area
of antenna is inclined at 47º with the direction of Earth’s magnetic field. If
the magnitude of Earth’s field at that place is 40773.9 nT find the magnetic
flux linked with the antenna.
Solution
B = 40773.9 nT; θ = 90º – 47º
= 43°;
A = 3m2
We know that ΦB = BAcosθ

EXAMPLE 4.2
A circular loop of area
5 x 10-2m2 rotates in a uniform magnetic field of 0.2 T.
If the loop rotates about its diameter which is perpendicular to the magnetic
field as shown in figure. Find the magnetic flux linked with the loop when its
plane is (i) normal to the field (ii) inclined 60o to the field and (iii)
parallel to the field.
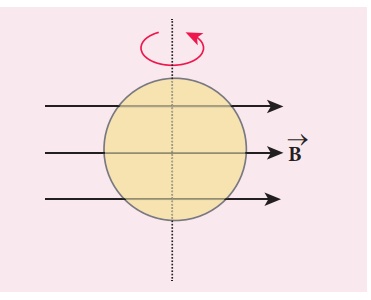
Solution
A = 5 ´ 10-2
m2; B = 0.2 T
(i) θ = 0°
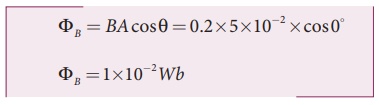
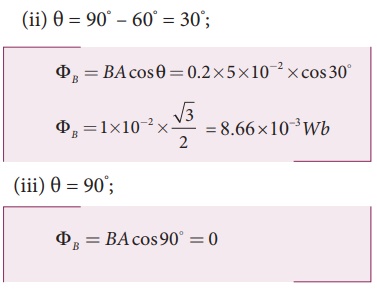
Related Topics