Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current
Power In AC Circuits
POWER IN AC CIRCUITS
1. Introduction of power in AC circuits
Power of a circuit is
defined as the rate of consumption of electric energy in that circuit. It is given by the
product of the voltage and current. In an AC circuit, the voltage and
current vary continuously with time. Let us first calculate the power at an
instant and then it is averaged over a complete cycle.
The alternating voltage
and alternating current in the series RLC circuit at an instant are
given by
v=Vm sin Žēt
andŌĆé i = I m sin( Žē t + Žå)
where ŽĢ is the
phase angle between Žģ and i. The instantaneous power is then
written as
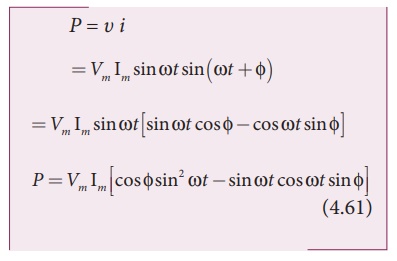
Here the average of sin2 Žēt over a cycle is 1/2 and that of sin Žē t cos Žēt is zero. Substituting these values, we obtain average power over a cycle.
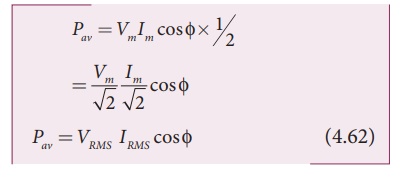
where VRMS
IRMS is called apparent power and cos ŽĢ is power
factor. The averagezpower of an AC circuit is also known as the true power of
the circuit.
Special Cases
(i) For a purely
resistive circuit, the phase angle between voltage and current is zero and cos ŽĢ
= 1.
Ōł┤ Pav = VRMS IRMS
(ii) For a purely
inductive or capacitive circuit, the phase angle is ┬▒ ŽĆ/2 and cos(┬▒ ŽĆ/2)=0.
Ōł┤ Pav = 0
(iii) For series RLC circuit, the phase angle
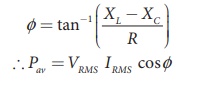
(iv) For series RLC circuit at
resonance, the phase angle is zero and
cos . ŽĢ =1
Ōł┤ Pav = VRMS IRMS
2. Wattless current
Consider an AC circuit
in which there is a phase angle of ŽĢ between VRMS and IRMS
and voltage is assumed to be leading the current by ŽĢ as shown in the
phasor diagram (Figure 4.55).
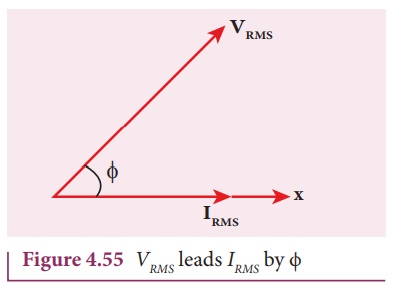
Now, IRMS
is resolved into two perpendicular components namely, IRMS
cos Žå along VRMS
and IRMS sin Žå
perpendicular to VRMS as shown in Figure 4.56.
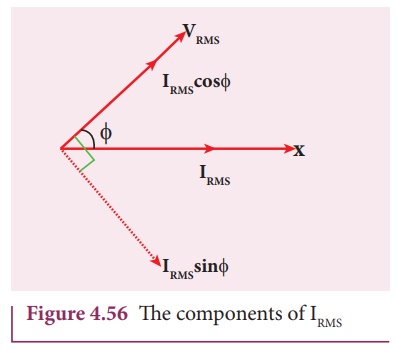
(i) The component of
current ( I RMS
cos Žå) which is in phase with
the voltage is called active component. The power consumed by this current VRMS
IRMS cos Žå . So that it is also known
as ŌĆśWattfulŌĆÖ current.
(ii) The other component
( I RMS
sin Žå) which has a phase angle
of ŽĆ/2 with the voltage
is called reactive component. The power consumed is zero. So that it is also
known as ŌĆśWattlessŌĆÖ current.
The current in an AC
circuit is said to be wattless current if the power consumed by it is zero.
This wattless current happens in a purely inductive or capacitive circuit.
3. Power factor
The power factor of a
circuit is defined in one of the following ways:
(i) Power factor =
cos ŽĢ = cosine of the angle of lead or lag
(ii) Power factor =
R/Z =
Impedance / Resistance
(iii) Power factor =
VI cos Žå / VI
= True power / Apparent power
Some examples for power
factors:
(i) Power factor = cos
0┬░ = 1 for a pure resistive circuit because the phase angle ŽĢ between
voltage and current is zero.
(ii) Power factor =
cos(┬▒ŽĆ /2 )= 0 for a purely inductive or capacitive circuit because the phase
angle ŽĢ between voltage and current is ┬▒ŽĆ /2 .
(iii) Power factor lies
between 0 and 1 for a circuit having R, L and C in varying
proportions.
4. Advantages and disadvantages of AC over DC
There are many
advantages and disadvantages of AC system over DC system.
Advantages:
(i) The generation of AC
is cheaper than that of DC.
(ii) When AC is supplied
at higher voltages, the transmission losses are small compared to DC
transmission.
(iii) AC can easily be
converted into DC with the help of rectifiers.![]()
![]()
Disadvantages:
(i) Alternating voltages
cannot be used for certain applications e.g. charging of batteries,
electroplating, electric traction etc.
(ii) At high voltages,
it is more dangerous to work with AC than DC.
EXAMPLE 4.26
A series RLC circuit
which resonates at 400 kHz has 80 ╬╝H inductor, 2000 pF capacitor and 50 ╬®
resistor. Calculate (i) Q-factor of the circuit (ii) the new value of
capacitance when the value of inductance is doubled and (iii) the new Q-factor.
Solution
L = 80 ├Ś 10-6H;
C = 2000 ├Ś 10-12 F
R = 50 ╬®; fr = 400 ├Ś 103Hz
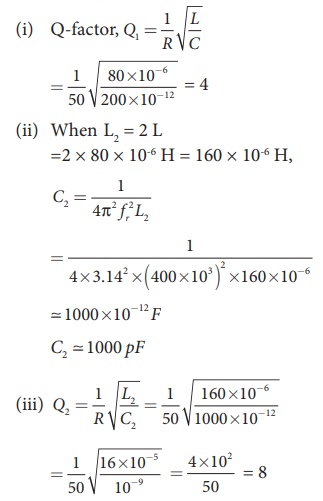
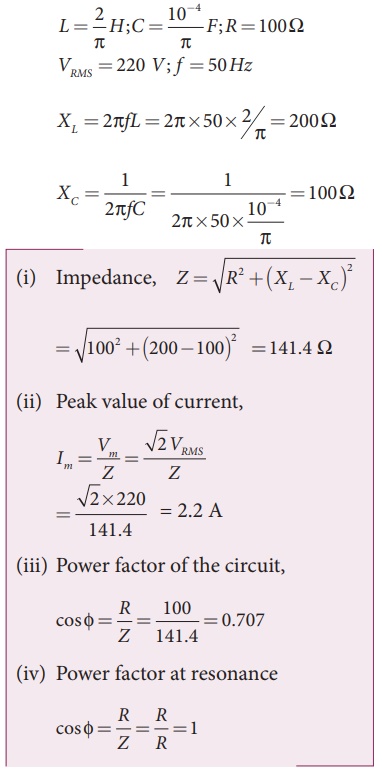
EXAMPLE 4.27
A capacitor of
capacitance 10-4 /ŽĆ F, an inductor of inductance 2/ ŽĆ H and a
resistor of resistance 100 ╬® are connected to form a series RLC circuit. When
an AC supply of 220 V, 50 Hz is applied to the circuit, determine (i) the
impedance of the circuit (ii) the peak value of current flowing in the circuit
(iii) the power factor of the circuit and (iv) the power factor of the circuit
at resonance.
Solution
Related Topics