Applications of Vector Algebra - Summary | 12th Mathematics : UNIT 6 : Applications of Vector Algebra
Chapter: 12th Mathematics : UNIT 6 : Applications of Vector Algebra
Summary
SUMMARY
1. For a given set of three vectors ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() , the scalar (
, the scalar (![]() ×
× ![]() ).
).![]() is
called a scalar triple product of
is
called a scalar triple product of ![]() ,
,![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
2. The volume of the parallelepiped formed by using the three vectors ,![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() co-terminus edges is given by |(
co-terminus edges is given by |(![]() ×
× ![]() ).
).![]() |.
|.
3. The scalar triple product of three
non-zero vectors is zero if and only if the three vectors are coplanar.
4. Three vectors ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() are
coplanar, if, and only if there exist scalars r, s, t ∈ R such that atleast one of them is non-zero and r
are
coplanar, if, and only if there exist scalars r, s, t ∈ R such that atleast one of them is non-zero and r![]() + s
+ s![]() + t
+ t![]() =
= ![]() .
.
5. If ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are any two systems of three vectors, and if
are any two systems of three vectors, and if
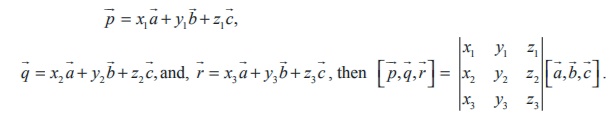
6. For a given set of three vectors ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , the vector
, the vector ![]() ×(
×(![]() ×
× ![]() ) is called vector triple product .
) is called vector triple product .
7. For any three vectors ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() we have
we have ![]() ×(
×(![]() ×
× ![]() ) = (
) = (![]() .
. ![]() )
)![]() - (
- (![]() .
.![]() )
)![]() .
.
8. Parametric form of the vector
equation of a straight line that passes through a given point with position
vector ![]() and parallel to a given vector
and parallel to a given vector ![]() is
is ![]() =
= ![]() + t
+ t![]() ,
where t ∈ R.
,
where t ∈ R.
9. Cartesian equations of a straight
line that passes through the point ( x1 , y1 , z1
) and parallel to a vector with direction ratios b1 , b2
, b3 are 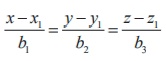 .
.
10. Any point on the line 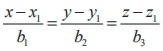 is
of the form ( x1 + tb1 , y1 + tb2 ,
z1 + tb3 ) , t ∈
R.
is
of the form ( x1 + tb1 , y1 + tb2 ,
z1 + tb3 ) , t ∈
R.
11. Parametric form of vector equation
of a straight line that passes through two given points with position vectors ![]() and
and ![]() is
is 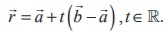 .
.
12. Cartesian equations of a line that
passes through two given points ( x1 , y1 , z1
) and ( x2 , y2 , z2 ) are 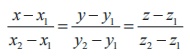
13. If θ is the acute angle between two
straight lines ![]() =
= ![]() + s
+ s![]() and
and ![]() =
= ![]() + td , then
+ td , then 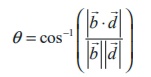
14. Two lines are said to be coplanar if
they lie in the same plane.
15. Two lines in space are called skew lines if they are not parallel and
do not intersect
16. The shortest distance between the
two skew lines is the length of the line segment perpendicular to both the skew
lines.
17. The shortest distance between the
two skew lines 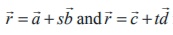 is
is
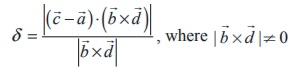
18. Two straight lines ![]() =
= ![]() + s
+ s![]() and
and ![]() =
= ![]() + t
+ t![]() intersect each other if (
intersect each other if (![]() -
- ![]() ).(
).(![]() × d ) = 0
× d ) = 0
19. The shortest distance between the
two parallel lines 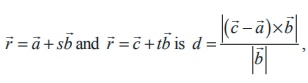 where |
where | ![]() | ≠ 0
| ≠ 0
20. If two lines 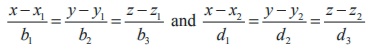 intersect, then
intersect, then 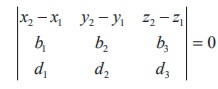
21. A straight line which is
perpendicular to a plane is called a normal to the plane.
22. The equation of the plane at a
distance p from the origin and perpendicular to the unit normal vector ![]() is
is ![]() .
.![]() = p ( normal form)
= p ( normal form)
23. Cartesian equation of the plane in
normal form is lx + my + nz = p
24. Vector form of the equation of a
plane passing through a point with position vector ![]() and
perpendicular to
and
perpendicular to ![]() is (
is (![]() -
- ![]() ).
). ![]() = 0.
= 0.
25. Cartesian equation of a plane normal
to a vector with direction ratios a,b,c and passing through a given point ( x1
, y1 , z1 ) is a ( x - x1 ) + b ( y - y1
) + c ( z - z1 ) = 0 .
26. Intercept form of the equation of
the plane ![]() .
. ![]() = q , having intercepts a, b, c on the x, y, z axes
respectively is
= q , having intercepts a, b, c on the x, y, z axes
respectively is 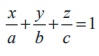 .
.
27. Parametric form of vector equation
of the plane passing through three given non-collinear points is 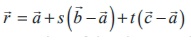
28. Cartesian equation of the plane
passing through three non-collinear points is
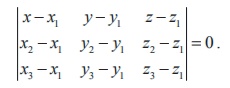
29. A straight will lie on a plane if
every point on the line, lie in the plane and the normal to the plane is
perpendicular to the line.
30. The two given non-parallel lines ![]() =
=
![]() + s
+ s![]() and
and ![]() =
= ![]() + t
+ t![]() are coplanar if (
are coplanar if (![]() -
- ![]() ).(
).(![]() ×
× ![]() )
= 0 .
)
= 0 .
31. Two lines 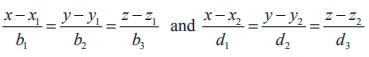 are
coplanar if
are
coplanar if 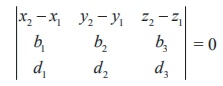
32. Non-parametric form of vector
equation of the plane containing the two coplanar lines ![]() =
= ![]() + t
+ t![]() and
and ![]() =
= ![]() + t
+ t![]() is (
is (![]() -
- ![]() ).(
).(![]() ×
× ![]() ) = 0 or (
) = 0 or (![]() -
- ![]() ).(
).(![]() ×
× ![]() ) = 0.
) = 0.
33. The acute angle θ between the two
planes 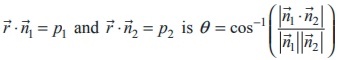 .
.
34. If θ is the acute angle between the
line ![]() =
= ![]() + t
+ t![]() and the plane
and the plane 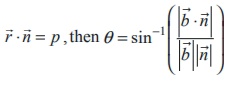
35. The perpendicular distance from a
point with position vector ![]() to the plane
to the plane ![]() .
.![]() = p is given by
= p is given by 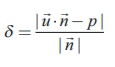
36. The perpendicular distance from a
point (x2 , y1, z1 ) to the plane ax + by + cz
= p is 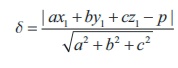
37. The perpendicular distance from the
origin to the plane ax + by + cz + d = 0 is given by 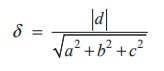
38. The distance between two parallel
planes ax + by + cz + d1 = 0 and ax + by + cz + d2 = 0 is
given by 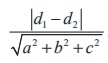
39. The vector equation of a plane which passes through the line of intersection of the planes
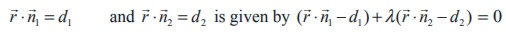
, where λ ∈ R is an.
40. The equation of a plane passing
through the line of intersection of the planes a1 x + b1 y + c1 z = d1 and
a2 x + b2 y + c2
z = d2 is given by
(a1
x + b1 y + c1 z - d1 ) + λ(a2 x + b2
y + c2 z - d2 ) = 0
41. The position vector of the point of
intersection of the line ![]() =
= ![]() + tb and the plane
+ tb and the plane ![]() =
= ![]() = p is
= p is 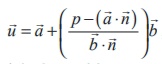 , where
, where ![]() .
.![]() ≠
≠ ![]() .
.
42. If ![]() is the position
vector of the image of
is the position
vector of the image of ![]() in the plane
in the plane ![]() .
. ![]() = p ,then
= p ,then 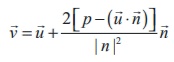
Related Topics