Chapter: 12th Mathematics : UNIT 6 : Applications of Vector Algebra
Equation of a plane perpendicular to a vector and passing through a given point
Equation
of a plane perpendicular to a vector and passing through a given point
(a) Vector form of equation
Consider a plane passing through a point A with position
vector ![]() and
and ![]() is a normal vector to the given plane.
is a normal vector to the given plane.
Let ![]() be the position vector of an
arbitrary point P on the plane.
be the position vector of an
arbitrary point P on the plane.
Then ![]() is perpendicular to
is perpendicular to ![]() .
.
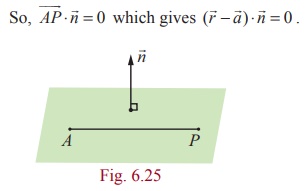
which is the vector form of the equation of a plane passing
through a point with position vector ![]() and perpendicular to
and perpendicular to ![]() .
.
Note
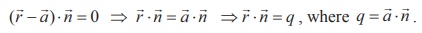
(b) Cartesian form of equation
If a, b, c are the direction ratios of ![]() ,
then we have
,
then we have ![]() = aiˆ + bˆj + ckˆ.
= aiˆ + bˆj + ckˆ.
Suppose, A is (x1 , y1
, z1) then equation (1) becomes ((x − x1
)iˆ + ( y − y1 ) ˆj + (z − z1
)kˆ) ⋅ (aiˆ + bˆj + ckˆ) =
0 . That is,
a(x − x1) + b( y − y1)
+ c(z − z1) = 0
which is the Cartesian equation of a plane, normal to a vector with direction ratios a, b, c and passing through a given point (x1 , y1 , z1) .
Related Topics