Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 11 : Waves
Summary - Physics: Waves
SUMMARY
A
disturbance which carries energy and momentum from one point in space to
another point in space without the transfer of medium is known as a wave.
The
waves which require medium for their propagation are known as mechanical waves.
The
waves which do not require medium for their propagation are known as
non-mechanical waves.
For
a transverse wave, the vibration of particles in a medium is perpendicular to
the direction of propagation of the wave.
For
a longitudinal wave, the vibration of particles in a medium is parallel to the
direction of propagation of the wave.
Elasticity
and inertia are necessary properties of the medium for wave propagation.
Waves
formed in still water (ripples) are transverse and wave formed due to vibration
of tuning fork is longitudinal.
The
distance between two consecutive crests or troughs is known as wavelength, λ.
The
number of waves which crossed a point per second is known as frequency, f.
The
time taken by one wave to cross a point is known as time period, T.
Velocity
of the wave is v = λf.
Frequency
is source dependent and wave velocity is medium dependent.
The
velocity of a transverse wave produce in a stretched string depends on tension
in the string and mass per unit length.
It does not depend on shape of the wave form.
Velocity
of transverse wave on a string is v 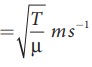 .
.
Velocity
of longitudinal wave in an elastic medium is v 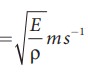
The minimum distance from a sound reflecting wall to hear an echo
at 20°C is 17.2 meters.

When
we superimpose two or more waves with slightly different frequencies then a
sound of periodically varying amplitude at a point is observed. This phenomenon
is known as beats. The number of amplitude maxima per second is called beat
frequency.
If
natural frequencies are written as integral multiples of fundamental frequency,
then the frequencies are said to be in harmonics. Thus, the first harmonic is v1 = v1, (the fundamental frequency is called first
harmonics), the second harmonics is v2 = 2
v1, the third harmonics is
v3 = 3 v1,
and so on.
Loudness of sound is defined as “the degree of sensation of sound produced in the ear or the
perception of sound by the listener”.
The intensity of sound is defined as “the sound power transmitted per unit area placed normal to the
propagation of sound wave ”.
Sound intensity level, 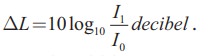
A closed organ pipe has only odd harmonics and the corresponding
frequency of the nth harmonic is fn = (2n + 1) f1.
In a closed organ pipe the frequencies of harmonics are in the
ratio f1 : f2 : f3 : f4 :... = 1 : 3 : 5 : 7 :...
The
open organ pipe has all harmonics and frequency of the nth harmonic is fn
= n f1.
In
the open organ pipe the frequencies of harmonics are in the ratio
f1 : f2 :
f3 : f4 :... = 1 : 2 : 3 : 4 :...
When
the source and the observer are in relative motion with respect to the medium
in which sound propagates, the frequency of the sound wave observed is
different from the frequency of the source. This phenomenon is called Doppler
Effect. The frequency received by the observer is known as apparent frequency.
When
the Source moves towards a stationary observer, the apparent frequency f ′= f (1+v/vs)

Related Topics