Physics - Introduction to Magnetism: Solved Example Problems | 12th Physics : Magnetism and Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Chapter: 12th Physics : Magnetism and Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Introduction to Magnetism: Solved Example Problems
Earth’s magnetic field and magnetic elements: Solved Example Problems
EXAMPLE 3.1
The horizontal component and vertical components of Earth’s magnetic field at a place are 0.15 G and 0.26 G respectively. Calculate the angle of dip and resultant magnetic field.
Solution:
BH = 0.15 G and BV = 0.26 G
tan I = 00.26/0.15 ⇒ I = tan −1(1. 732) =60º
The resultant magnetic field of the Earth is
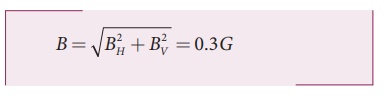
Basic properties of magnets: Solved Example Problems
EXAMPLE 3.2
Let the magnetic moment of a bar magnet be ![]() m whose magnetic length is d = 2l and pole strength is qm. Compute the magnetic moment of the bar magnet when it is cut into two pieces
m whose magnetic length is d = 2l and pole strength is qm. Compute the magnetic moment of the bar magnet when it is cut into two pieces
(a) along its length
(b) perpendicular to its length.
Solution
(a) a bar magnet cut into two pieces along its length:
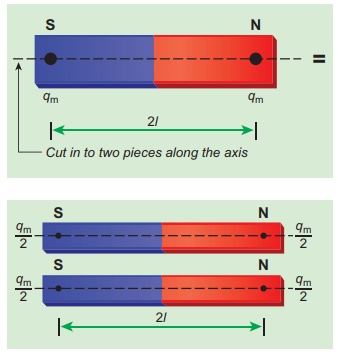
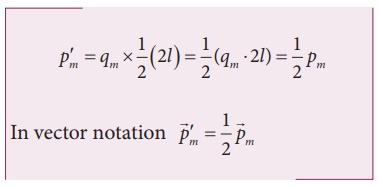
When the bar magnet is cut along the axis into two pieces, new magnetic pole strength is q′m = qm/2 but magnetic length does not change. So, the magnetic moment is
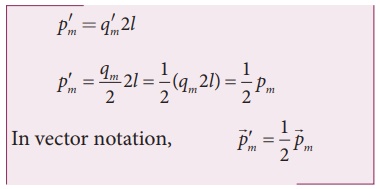
In vector notation,
(b) a bar magnet cut into two pieces perpendicular to the axis:
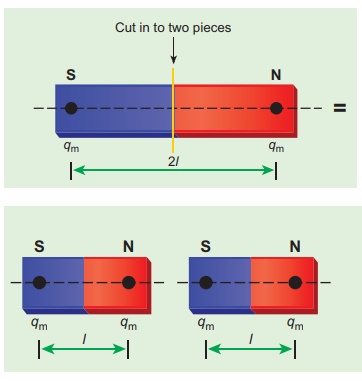
When the bar magnet is cut perpendicular to the axis into two pieces, magnetic pole strength will not change but magnetic length will be halved. So the magnetic moment is
EXAMPLE 3.3
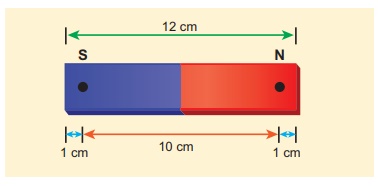
Compute the magnetic length of a uniform bar magnet if the geometrical length of the magnet is 12 cm. Mark the positions of magnetic pole points.
Solution
Geometrical length of the bar magnet is 12 cm
Magnetic length = 5/6 x (geometrical length)
= 5/6 x 12 = 10cm
In this figure, the dot implies the pole points.
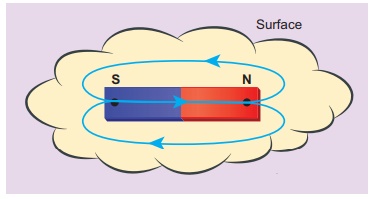
EXAMPLE 3.4
Calculate the magnetic flux coming out from the surface containing magnetic dipole (say, a bar magnet) as shown in figure.
Solution
Magnetic dipole is kept, the total flux emanating from the closed surface S is zero. So,
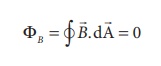
Here the integral is taken over closed surface. Since no isolated magnetic pole (called magnetic monopole) exists, this integral is always zero,
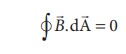
This is similar to Gauss’s law in electrostatics. (Refer unit 1)
Related Topics