Lorentz Force | Physics - Force on a moving charge in a magnetic field | 12th Physics : Magnetism and Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Chapter: 12th Physics : Magnetism and Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Force on a moving charge in a magnetic field
Force on a moving charge in a magnetic field
When an electric charge q is moving with velocity ![]() in the magnetic field
in the magnetic field ![]() , it experiences a force, called magnetic force
, it experiences a force, called magnetic force ![]() . After careful experiments, Lorentz deduced the force experienced by a moving charge in the magnetic field
. After careful experiments, Lorentz deduced the force experienced by a moving charge in the magnetic field ![]()
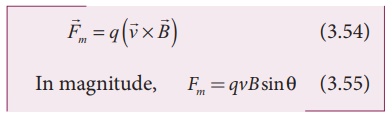
The equations (3.54) and (3.55) imply
1. ![]() is directly proportional to the magnetic field
is directly proportional to the magnetic field ![]()
2. ![]() is directly proportional to the velocity
is directly proportional to the velocity ![]()
3. ![]() is directly proportional to sine of the angle between the velocity and magnetic field
is directly proportional to sine of the angle between the velocity and magnetic field
4. ![]() is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge q
is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge q
5. The direction of ![]() is always perpendicular to
is always perpendicular to ![]() and
and ![]() as
as ![]() is the cross product of
is the cross product of ![]() and
and ![]()
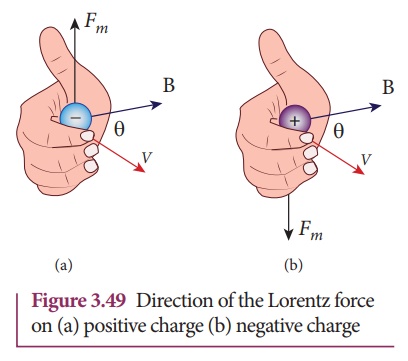
6. The direction of ![]() on negative charge is opposite to the direction of
on negative charge is opposite to the direction of ![]() on positive charge provided other factors are identical as shown Figure 3.49
on positive charge provided other factors are identical as shown Figure 3.49
7. If velocity ![]() of the charge q is along magnetic field
of the charge q is along magnetic field ![]() then,
then, ![]() is zero
is zero
Definition of tesla
The strength of the magnetic field is one tesla if unit charge moving in it with unit velocity experiences unit force.
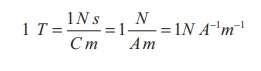
EXAMPLE 3.20
A particle of charge q moves with along positive y - direction invelocity ![]() a magnetic field
a magnetic field ![]() . Compute the Lorentz force experienced by the particle (a) when magnetic field is along positive y-direction (b) when magnetic field points in positive z - direction (c) when magnetic field is in zy - plane and making an angle θ with velocity of the particle. Mark the direction of magnetic force in each case.
. Compute the Lorentz force experienced by the particle (a) when magnetic field is along positive y-direction (b) when magnetic field points in positive z - direction (c) when magnetic field is in zy - plane and making an angle θ with velocity of the particle. Mark the direction of magnetic force in each case.
Solution
Velocity of the particle is 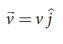
(a) Magnetic field is along positive y - direction, this implies, 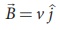
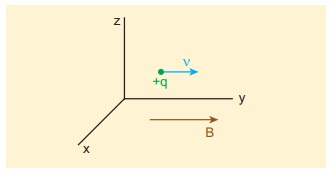
From Lorentz force, 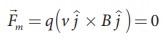
So, no force acts on the particle when it moves along the direction of magnetic field.
(b) Magnetic field points in positive z - direction, this implies, 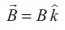
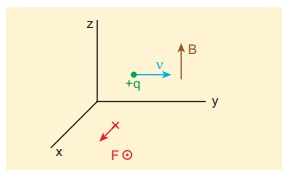
From Lorentz force,
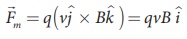
Therefore, the magnitude of the Lorentz force is qvB and direction is along positive x - direction.
(c) Magnetic field is in zy - plane and making an angle θ with the velocity of the particle, which implies 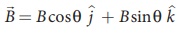
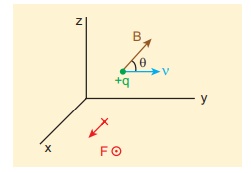
From Lorentz force,
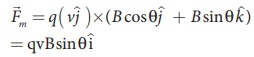
EXAMPLE 3.21
Compute the work done and power delivered by the Lorentz force on the particle of charge q moving with velocity ![]() . Calculate the angle between Lorentz force and velocity of the charged particle and also interpret the result.
. Calculate the angle between Lorentz force and velocity of the charged particle and also interpret the result.
Solution
For a charged particle moving on a magnetic field,
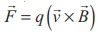
The work done by the magnetic field is
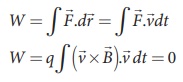
Since ![]() is perpendicular to
is perpendicular to ![]() and hence
and hence 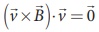 This means that Lorentz force do no work on the particle. From work kinetic energy theorem, (Refer section 4th chapter, XI th standard Volume I)
This means that Lorentz force do no work on the particle. From work kinetic energy theorem, (Refer section 4th chapter, XI th standard Volume I)
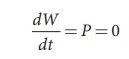
Since, 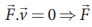 and
and ![]() are perpendicular to each other. The angle between Lorentz force and velocity of the charged particle is 90º. Thus Lorentz force changes the direction of the velocity but not the magnitude of the velocity. Hence Lorentz force does no work and also does not alter kinetic energy of the particle.
are perpendicular to each other. The angle between Lorentz force and velocity of the charged particle is 90º. Thus Lorentz force changes the direction of the velocity but not the magnitude of the velocity. Hence Lorentz force does no work and also does not alter kinetic energy of the particle.
Related Topics