Chapter: 12th Physics : Magnetism and Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Conversion of galvanometer into ammeter and voltmeter
Conversion
of galvanometer into ammeter and voltmeter
A galvanometer is very
sensitive instrument to detect the current. It can be easily converted into
ammeter and voltmeter.
Galvanometer to an Ammeter
Ammeter is an instrument
used to measure current flowing in the electrical circuit. The ammeter must
offer low resistance such that it will not change the current passing through
it. So ammeter is connected in series to measure the circuit current.
A galvanometer is
converted into an ammeter by connecting a low resistance in parallel with the
galvanometer. This low resistance is called shunt resistance S. The scale is
now calibrated in ampere and the range of ammeter depends on the values of the
shunt resistance.
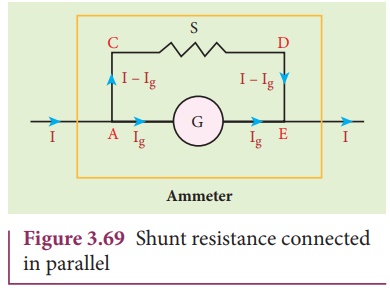
Let I be the current
passing through the circuit as shown in Figure 3.69. When current I reaches the
junction A, it divides into two components. Let Ig be the current
passing through the galvanometer of resistance Rg through a path AGE
and the remaining current (I ŌĆō Ig) passes along the path ACDE
through shunt resistance S. The value of shunt resistance is so adjusted that
current Ig produces full scale deflection in the galvanometer. The
potential difference across galvanometer is same as the potential difference
across shunt resistance.
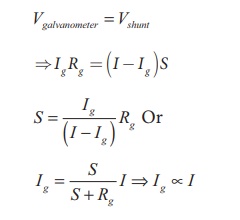
Since, the deflection in
the galvanometer is proportional to the current passing through it.
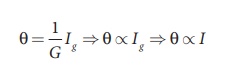
So, the deflection in
the galvanometer measures the current I passing through the circuit (ammeter).
Shunt resistance is
connected in parallel to galvanometer. Therefore, resistance of ammeter can be
determined by computing the effective resistance, which is
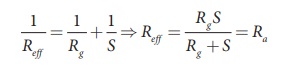
Since, the shunt
resistance is a very low resistance and the ratio S/ Rg is
also small. This means, Rg is also small, i.e., the
resistance offered by the ammeter is small. So, when we connect ammeter in
series, the ammeter will not change the resistance appreciably and also the
current in the circuit. For an ideal ammeter, the resistance must be equal to
zero. Hence, the reading in ammeter is always lesser than the actual current in
the circuit. Let Iideal be current measured from ideal ammeter and Iactual
be the actual current measured in the circuit by the ammeter.![]()
![]()
Then, the percentage
error in measuring a current through an ammeter is
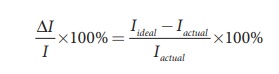
Key points
1. An ammeter is a low
resistance instrument and it is always connected in series to the circuit
2. An ideal ammeter has
zero resistance
3. In order to increase
the range of an ammeter n times, the value of shunt resistance to be connected
in parallel is S =G/n-1
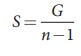
Galvanometer to a voltmeter
A voltmeter is an
instrument used to measure potential difference across any two points in the electrical
circuits. It should not draw any current from the circuit otherwise the value
of potential difference to be measured will change.
Voltmeter must have high
resistance and when it is connected in parallel, it will not draw appreciable
current so that it will indicate the true potential difference.
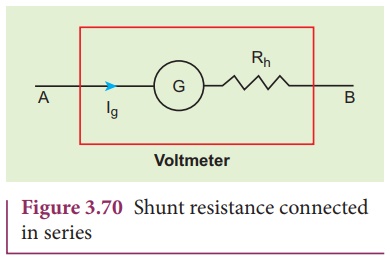
A galvanometer is
converted into a voltmeter by connecting high resistance Rh in
series with galvanometer as shown in Figure 3.74. The scale is now calibrated
in volt and the range of voltmeter depends on the values of the resistance
connected in series i.e. the value of resistance is so adjusted that only
current Ig produces full scale deflection in the galvanometer.
Let Rg be the
resistance of galvanometer and Ig be the current with which the
galvanometer produces full scale deflection. Since the galvanometer is
connected in series with high resistance, the current in the electrical circuit
is same as the current passing through the galvanometer.
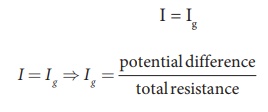
Since the galvanometer
and high resistance are connected in series, the total resistance or effective
resistance gives the resistance of voltmeter. The voltmeter resistance is
Rv = Rg +Rh
Therefore,
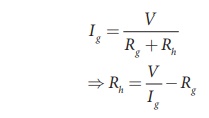
Note that I g ŌłØV
The deflection in the
galvanometer is proportional to current Ig. But current Ig
is proportional to the potential difference. Hence the deflection in the
galvanometer is proportional to potential difference. Since the resistance of
voltmeter is very large, a voltmeter connected in an electrical circuit will
draw least current in the circuit. An ideal voltmeter is one which has infinite
resistance.
Key points
1. Voltmeter is a high
resistance instrument and it is always connected in parallel with the circuit
element across which the potential difference is to be calculated
2. An ideal voltmeter has
infinite resistance
3. In order to increase
the range of voltmeter n times the value of resistance to be connected in
series with galvanometer is R = (n-1) G
Related Topics