Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 7 : Properties of Matter
Factors affecting the surface tension of a liquid
Factors
affecting the surface tension of a liquid
Surface
tension for a given liquid varies in following situations
(1) The presence of any contamination or impurities considerably affects the force of
surface tension depending upon the degree of contamination.
(2) The presence of dissolved substances can also affect the value of surface
tension. For example, a highly soluble substance like sodium chloride (NaCl) when dissolved in water (H20) increases the surface
tension of water. But the sparingly soluble substance like phenol or soap
solution when mixed in water decreases the surface tension of water.
(3) Electrification affects the surface tension. When a liquid is
electrified, surface tension decreases. Since external force acts on the liquid
surface due to electrification, area of the liquid surface increases which acts
against the contraction phenomenon of the surface tension. Hence, it decreases.
(4) Temperature plays
a very crucial role in altering the surface tension of a
liquid. Obviously, the surface tension decreases linearly with the rise of
temperature. For a small range of temperature, the surface tension at Tt at t ┬║C is Tt = T0 (1ŌłÆ ╬▒ t)
Where,
T0 is the surface tension
at temperature 0┬║C and ╬▒ is the
temperature coefficient of surface tension. It is to be noted that at the
critical temperature, the surface tension is zero as the interface between
liquid and vapour disappear. For example, the critical temperature of water is
374┬║C. Therefore, the surface tension of water is zero at that temperature. van
der Wall suggested the important relation between the surface tension and the
critical temperature as
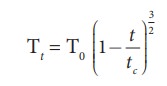
Generalizing
the above relation, we get
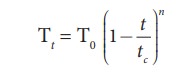
which
gives more accurate value. Here n, varies for different liquids and t and tc
denotes the temperature and critical temperature in absolute scale (Kelvin
scale), respectively.
Related Topics