Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Paediatrics
The Blue Baby - Heart Disease in Children
Heart Disease in Children
The Blue Baby
·
Neonatal adaptation:
o With first breath:
§ Alveolar oxygen tension increases
§ Pulmonary bed dilates
o Ductus arteriosus starts to constrict
· Cord clamp:
o In LV
and LA pressure
o Functional closure of foramen ovale
·
Ductus: closes at 24 – 48 hours.
A murmur may be normal. Can open or close it with drugs (NSAIDS close, prostaglandins
open)
·
Replacement of HbF with HbA from
24 weeks (90%) to birth (70%) to 6 months (trace)
Clinical Signs of Heart Disease
·
Clinical warning signs:
o Early murmurs in a clinically well baby
o New-born who becomes hypoxic
·
Classifying:
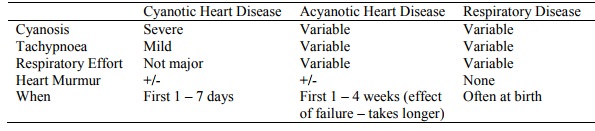
Causes of Cyanosis
· Respiratory Causes:
o Hypoventilation: Central apnoea from drugs, apnoea of prematurity, sepsis, metabolic (eg hypoglycaemia), seizures
o Mechanical interference with lung function: airway obstruction,
abdominal distension, pneumothorax, thoracic and sternal deformities, etc
o V-Q mismatch with lung disease:
§ Infection (Gp B Strep, G – ive): pneumonia on X-ray hard to distinguish from wet-lung of early respiratory distress. Have high index of suspicion, low threshold for antibiotics
§ Respiratory Distress Syndrome: X-ray appearance: Ground glass + air bronchogram Þ ¯surfactant. If maternal diabetes, are deficient in surfactant until later in gestation
§ Aspiration: meconium, milk, blood
§ Pulmonary oedema, hydrops fetalis (Þ in heart failure before delivery. Used to be due to Rhesus negative disease prior to Anti-D treatment, now numerous other causes)
§ Lung haemorrhage: complication in premature
§ Primary lung disease
·
Cardiac causes of cyanosis:
o R to L shunt: Cyanotic heart disease or pulmonary hypertension
o L to R shunt and Heart failure
·
Differentiating Heart and Lung
Disease:
o History and exam:
§ When did it start
§ Relationship of cyanosis to birth. If heart, pink to start with then go blue as ductus closes (blood gets to lungs via reverse flow through ductus if right heart not functioning well)
§ Check respiration:
·
If apnoea Þ
heart. If heart problems, won‟t work so
hard at breathing
·
Respiratory distress and effort Þ airway
or lung problem
o By investigations:
§ CXR (heart size, lung fields)
§ ABG/O2 saturation monitoring. If lung disease, may have CO2
§ Hyperoxia test: put in 100% O2 – if heart disease then won‟t change PO2
as gas transfer is not the problem
§ Echocardiography
·
Also consider sepsis and anaemia
Related Topics