Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Paediatrics
Childhood Cancer
Childhood Cancer
·
Cancer: 10% of childhood deaths,
most common cause of death after accidents Þ have high index of suspicion
·
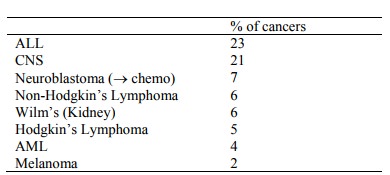
Distribution:
·
Signs and Symptoms:
o Often non specific
o Adult symptoms rare, eg epistaxis, dysphagia, non healing lesion, rectal
bleeding, change in bowel habit
o Para-neoplastic syndromes are rare
·
Headaches warranting
investigation. Headaches are common, but
watch out for:
o Recurrent morning headaches
o One that awakens the child
o Intense and incapacitating
o Headaches that change in quality, frequency and pattern (eg getting more
frequent)
o Focal signs or ataxia
o MRI more sensitive than CT
·
Lymphadenopathy:
o Common finding in cervical, axillary and inguinal chains. Usually < 1
cm
o Most enlarged nodes are due to infection
o Suspicious if found in mediastinum, posterior auricular, epitrochlear
and supraclavicular
·
Bone and Joint Pain:
o Early symptoms rarely include pain – except in bone (bone cancer and malignancy)
o Usually no pathognomic signs on Xray ® need biopsy
·
Pancytopaenia:
o Common finding in ALL and AML
o Need neutrophil count specifically.
Lymphocytes may mask ¯neutrophils.
o From 6 months to puberty, anaemia is 110 g/L. 50% of leukaemia presents with Hb < 75 g/L
o Involvement of two or more lines ® bone marrow evaluation
·
Leukocytosis: Common in AML and
ALL. But count may get up to 50,000 with septicaemia and some viruses, also in
Down syndrome and post-natal
·
Presenting signs of cancer:
o Recurrent bone pain, paleness, weight loss: leukaemia
o Morning headache with vomiting: brain tumour (usually a migraine)
o Lump in neck not responsive to antibiotics: Lymphoma
o White dot in new born eye: Retinoblastoma
o Proptosis (bulging eye): Leukaemia, neuroblastoma
o Swollen face and neck: lymphoma, leukaemia (compression of veins)
o Abdominal mass: Wilm‟s, neuroblastoma, liver & spleen enlargement in
leukaemia
o Cough, stridor, haemoptasis, Horner‟s: Mediastinal tumour
·
Diagnosis: tumour markers (only
in neuroblastoma: catecholamine), imaging, bone scan, biopsy
Related Topics