Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Paediatrics
Examination - Paediatrics
Examination
·
Principles:
o Leave nasty things till last
o Observe
o Get on floor and use games
o Wait until child familiar with environment but start before bored
o Don‟t touch child until rapport established
o Use your own toys – they‟re novel
o Get parents to undress them (or do anything else that is nasty)
o Get them to draw pictures while taking the history
·
They‟re likely to be scared
(depending on previous experience). Build rapport, play games, talk with child
not through parent. Don‟t wear stethoscope around neck
·
Show them what you want rather
than telling them
·
Blood pressure:
o Is important – always do it
o Getting them calm is hard – usually anxious ®
artefacts common
o Cuff: Bladder should nearly encircle the arm. Width is 2/3 length from should to elbow
· Chest exam:
o Percussion more sensitive than auscultation (won‟t show anything in the
absence of respiratory signs/symptoms)
o Percussion will tell you about hyperinflation, fluid, mediastinal shift
o Ausciltate heart early in the exam – but not first
·
Abdominal exam: Get child to suck
in and push out tummy to check for tenderness – then you won‟t have to hurt
them yourself.
· Differences in a baby:
o More liver in the abdomen (2 finger breaths is normal). Don‟t press too
hard – moves with respiration
o Pelvic organs higher (eg bladder)
o Pulses: Radial/ Brachial – take both sides. Must palpate femoral pulse.
If feet aren‟t white don‟t take peripheral pulses
·
Teenage girls: examine chest
underneath clothes
Normal Values
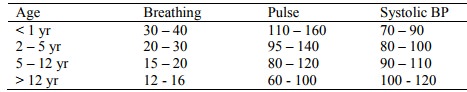
·
Stethoscope around your neck adds
10!
·
Haemoglobin: at birth: 170, day
5: 200, 12 weeks: 120 (lower limit of normal is 90 – 100)
Examination outline
·
Height, Weight and Head
Circumference (and plot them)
·
General:
o Sick or well
o Dysmorphic features
o Obvious distress
o Temperature
o Colour/rashes/anaemia/cyanosis/jaundice
o Lymph nodes: Check anterior and posterior cervical chains, subhyoid,
sub-occipital, sub-mandibular, sub-lingual, axillary, inguinal and epitrochlear
o Hydration/perfusion
·
Cardiovascular:
o Pulses: radial, femoral, synchrony, sinus arrhythmia (normal in all
children)
o Blood pressure (NB use correct cuff size)
o JVP: often hard to see
o Peripheral oedema (Periorbital in babies)
o Liver enlargement ® right ventricular failure
o Feel the cardiac impulse: Apex may be more lateral in children. Thrills
o Auscultation
·
Respiratory:
o Ears, throat, nose, sinuses
o Clubbing
o Chest deformity
o Respiratory rate, effort and accessory muscle use, grunting, ability to talk in sentences
o Intercostal, sub-sternal and supraclavicular indrawing, hyperinflation, Harrison‟s sulcus (lower ribs pulled in ® chronic airways disease), pigeon chest (Þ chronic in AP diameter), tracheal tug, nasal flaring
o Auscultation, including cardiac dullness (Þ
hyperinflation). Tracheal position
rarely of value
·
Abdominal:
o Inspection, movements, scars, hernia
o Liver, spleen and kidneys
o Bladder
o Masses
o Tenderness
o External genitalia
o Examine anus (PR rarely required)
·
Neurological:
o Developmental assessment: See Topic: Child Development
o Neurological Exam: See Topic: Neurological Exam in Children
·
Joints
·
Skin
Related Topics