Chapter: Modern Analytical Chemistry: Electrochemical Methods of Analysis
Potentiometric Biosensors - Potentiometric Methods of Analysis
Potentiometric Biosensors
Potentiometric electrodes for the analysis of molecules of biochemical importance can be constructed in a fashion
similar to that used for gas-sensing electrodes. The most
common class of potentiometric biosensors are the so-called enzyme
electrodes, in which
an enzyme is trapped or immobilized at the
surface of an ion-selective electrode. Reaction of the
analyte with the
enzyme produces a product
whose concentration is monitored by the ion-selective elec- trode. Potentiometric biosensors have also
been designed around
other biologi- cally active species, including
antibodies, bacterial particles, tissue, and hormone receptors.
One example of an enzyme
electrode is the urea electrode, which is based
on the catalytic hydrolysis of urea by urease
|
4 3 |
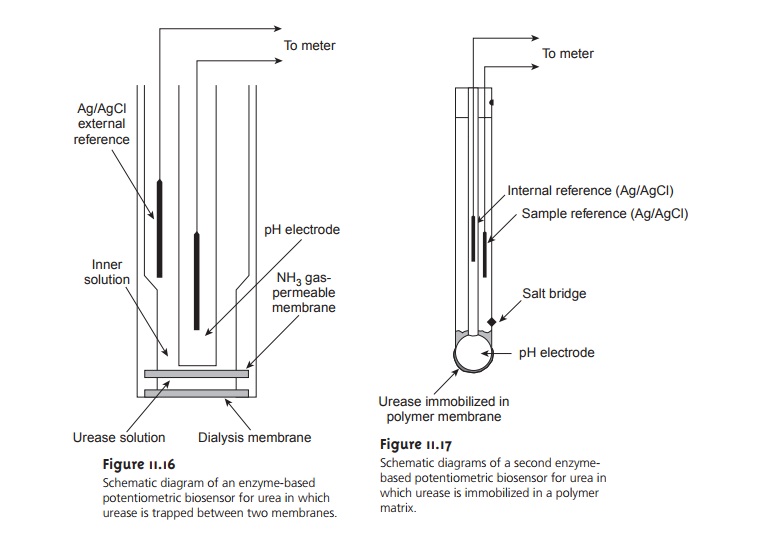
In one version of the urea electrode, shown in Figure 11.16, an NH3 electrode is modified by adding a dialysis membrane that physically traps a pH 7.0 buffered so- lution of urease between the dialysis membrane and the gas-permeable membrane.
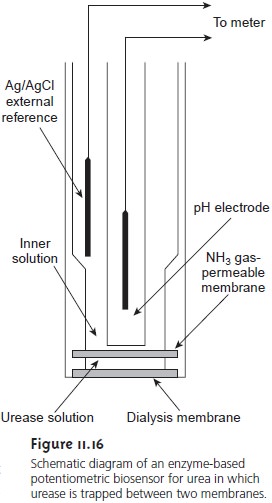
When immersed in the sample,
urea diffuses through
the dialy- sis membrane, where it reacts
with the enzyme
urease. The NH4+ that is pro-
duced is in equilibrium with NH3
NH4+(aq)+H O(l)
< == == > H3O+(aq)+ NH3
(aq)
which, in turn,
diffuses through the gas-permeable membrane, where it is de-
tected by a pH electrode. The response of the electrode to the concentration of urea is given
by
Ecell
= K – 0.05916 log [urea] ………….11.12
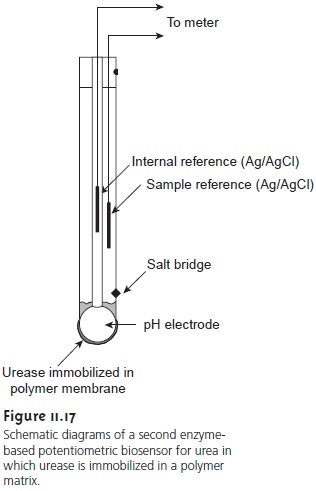
Another version of the urea electrode (Figure
11.17) immobilizes the enzyme
in a polymer membrane formed
directly on the tip of a glass
pH electrode.5 In this case, the electrode’s response is
pH = K [urea]
………….11.13
Few potentiometric biosensors are commercially available. As
shown in Figures 11.16 and 11.17,
however, available ion-selective and gas-sensing electrodes may be easily converted into biosensors.
Related Topics