Chapter: Modern Analytical Chemistry: Electrochemical Methods of Analysis
Gas-Sensing Electrodes - Potentiometric Methods of Analysis
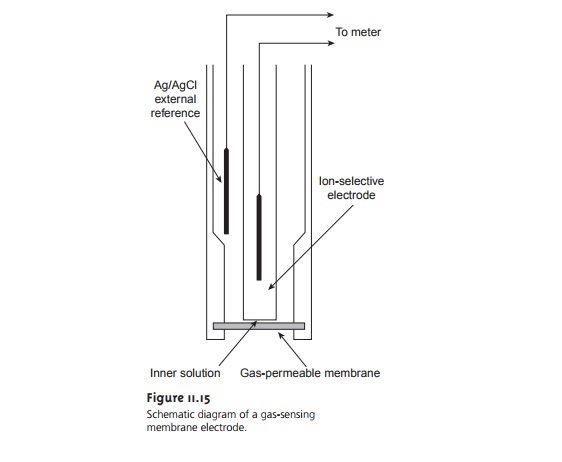
Gas-Sensing Electrodes
A number of membrane electrodes have been devel-
oped that respond
to the concentration of dissolved gases. The basic
design of these electrodes is shown in Figure 11.15
and consists of a thin
membrane sepa- rating the
sample from an inner solution containing an ion-selective electrode. The membrane is permeable to the gaseous
analyte, but is not permeable
to nonvolatile components in the sample
matrix. Once the
gaseous analyte passes
through the membrane, it reacts in the inner
solution, producing a species
whose concentration can be monitored by an appropriate ion-selective elec-
trode. For example, in the CO2 electrode, CO2 reacts in the inner
solution to produce H3O+.
|
3 |
The change in the concentration of H3O+ is monitored with a pH ion-selective electrode, for which the cell potential
is given by equation 11.9. The relation- ship between the concentration of H3O+ and CO2 is given
by rearranging the equilibrium constant expression for
reaction 11.10; thus
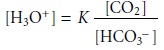 11.11
11.11
where K is the
equilibrium constant. If the amount of HCO3– in the internal solu
|
3 |
Ecell = K’ + 0.05916 log [CO2]
where K’ is a constant that includes the constant for the pH ion-selective electrode, the equilibrium constant for reaction 11.10,
and the concentration of HCO3–.
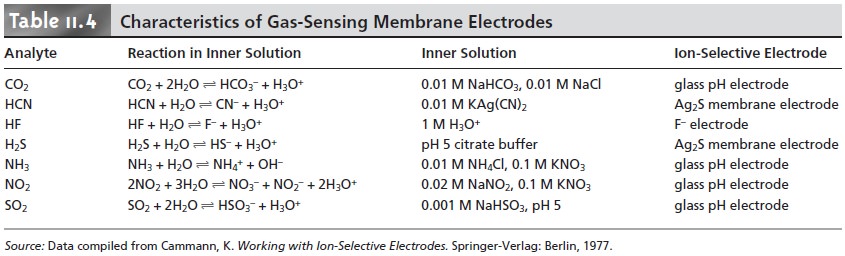
Gas-sensing electrodes have been developed
for a variety of gases, the charac- teristics for which are
listed in Table
11.4. The composition of the inner
solution changes with use,
and both it and the
membrane must be replaced periodically. Gas-sensing electrodes are stored in a solution
similar to the internal solution
to minimize their exposure to atmospheric gases.
Related Topics