Chapter: Modern Analytical Chemistry: Electrochemical Methods of Analysis
Liquid-Based Ion-Selective Electrodes - Potentiometric Methods of Analysis
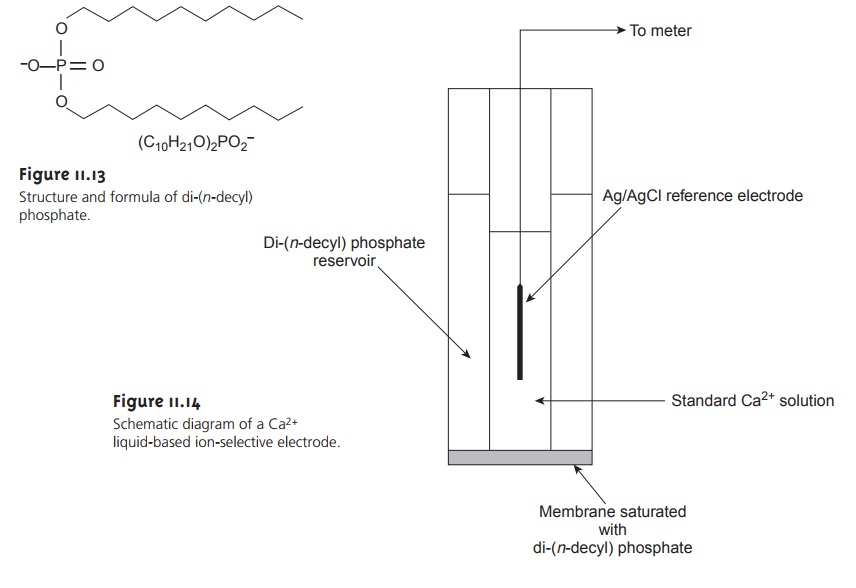
Liquid-Based Ion-Selective Electrodes
Another
approach
to
constructing an ion-selective electrode is to use a hydrophobic membrane containing a selective, liquid organic complexing agent. Three types
of organic liquids
have been used: cation exchangers, anion exchangers, and
neutral ionophores. When the ana- lyte’s concentration on the two
sides of the
membrane is different, a membrane
potential is the result. Current
is carried through
the membrane by the analyte.
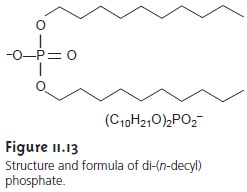
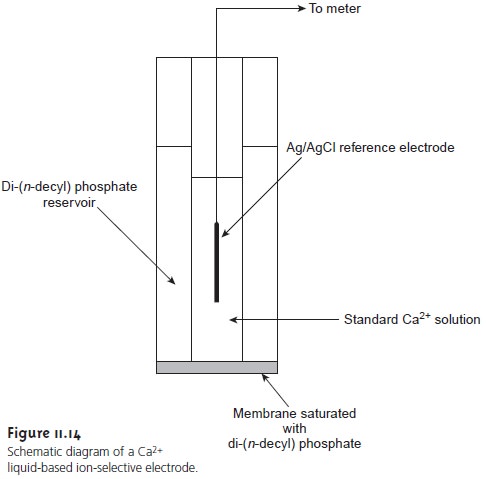
One example of a liquid-based ion-selective electrode is that for Ca2+, which uses a porous plastic membrane saturated with di-(n-decyl) phosphate (Figure 11.13). As shown in Figure 11.14, the membrane is placed at the end of a noncon- ducting cylindrical tube and is in contact with two reservoirs. The outer reservoir contains di-(n-decyl) phosphate in di-n-octylphenylphosphonate, which soaks into the porous membrane. The inner reservoir contains a standard aqueous solution of Ca2+ and a Ag/AgCl reference electrode. Calcium ion-selective electrodes are also available in which the di-(n-decyl) phosphate is immobilized in a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) membrane, eliminating the need for a reservoir containing di-(n-decyl) phosphate.
A membrane potential
develops as the result of a difference in the equilibrium position of the complexation reaction
|
2 |
on the two sides of the membrane,
where (m) indicates that the species
is present in the
membrane. The cell
potential for the
Ca2+ ion-selective electrode is
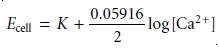
The selectivity of the electrode for Ca2+ is very good, with only Zn2+ showing
greater selectivity.
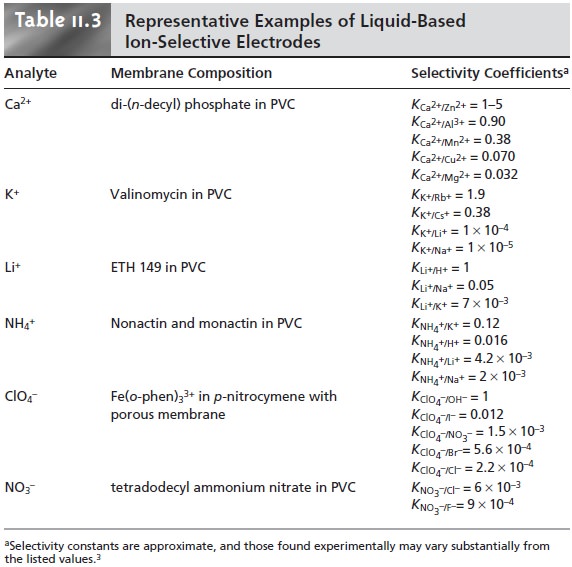
The properties of several representative liquid-based
ion-selective electrodes are presented in Table 11.3.
An electrode using
a liquid reservoir can be stored
in a dilute solution
of analyte and needs no additional conditioning before use. The life-
time of an electrode with a PVC membrane, however,
is proportional to its expo- sure to aqueous solutions. For this reason
these electrodes are best stored
by cover- ing the membrane
with a cap containing
a small amount of wetted gauze to maintain a humid environment. The
electrode must then be conditioned be- fore use by soaking in a solution of
analyte for 30–60 min.
Related Topics