Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 2 : Kinematics
Integral Calculus
INTEGRAL CALCULUS
Integration
is basically an area finding process. For certain geometric shapes we can
directly find the area. But for irregular shapes the process of integration is
used. Consider for example the areas of a rectangle and an irregularly shaped
curve, as shown in Figure 2.29.
The
area of the rectangle is simply given by A = length × breadth = (b-a) c
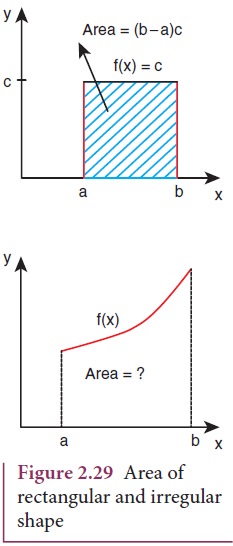
But
to find the area of the irregular shaped curve given by f(x), we divide the
area into rectangular strips as shown in the Figure 2.30.
The
area under the curve is approximately equal to sum of areas of each rectangular
strip.
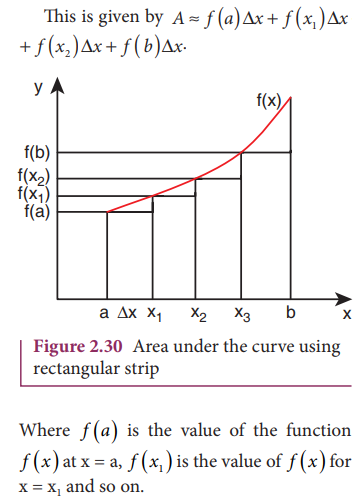
As
we increase the number of strips, the area evaluated becomes more accurate. If
the area under the curve is divided into N strips, the area under the curve is
given by

The
integration will give the total area under the curve f (x). This is shown in
Figure 2.31.
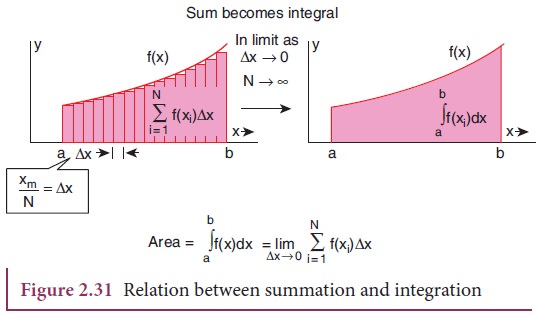
Examples
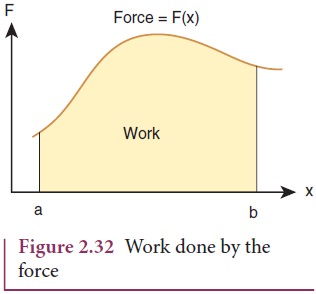
In
physics the work done by a force F(x)
on an object to move it from point a
to point b in one dimension is given
by
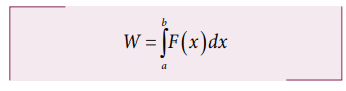
(No
scalar products is required here, since motion here is in one dimension)
1)
The work done is the area under the force displacement graph as shown in Figure
2.32
2)
The impulse given by the force in an interval of time is calculated between the
interval from time t = 0 to time t = t1 as
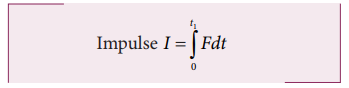
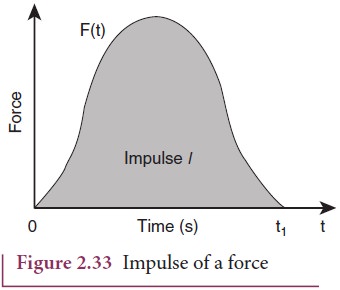
The
impulse is the area under the force function F (t) - t graph as shown in Figure
2.33.
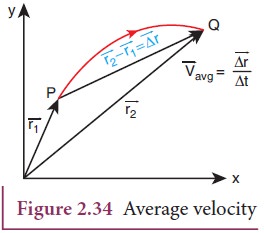
Average velocity
Consider
a particle located initially at point P having position vector ![]() . In a time interval ∆t the particle is moved to the point Q having position vector
. In a time interval ∆t the particle is moved to the point Q having position vector ![]() . The displacement vector is ∆
. The displacement vector is ∆![]() =
= ![]() −
− ![]() .
This is shown in Figure 2.34.
.
This is shown in Figure 2.34.
The
average velocity is defined as ratio of the displacement vector to the
corresponding time interval
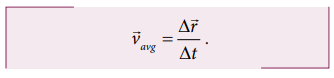
It
is a vector quantity. The direction of average velocity is in the direction of
the displacement vector (Δ![]() ).
).
This
is also shown in Figure 2.34.
Average speed
The
average speed is defined as the ratio of total path length travelled by the
particle in a time interval.
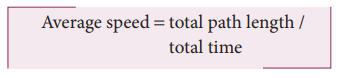
Instantaneous velocity or velocity
The instantaneous velocity at an
instant t or simply ‘velocity’ at an
instant t is defined as limiting
value of the average velocity as Δt → 0, evaluated at
time t.
In other words, velocity is equal to
rate of change of position vector with respect to time. Velocity is a vector
quantity.
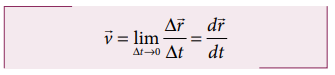
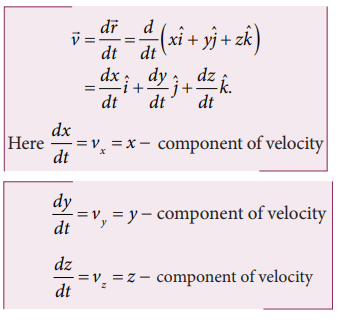
In component form, this velocity is
The magnitude of velocity v is called speed and is given by
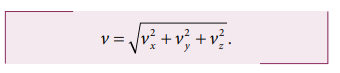
Speed
is always a positive scalar. The unit of speed is also m
Momentum
The linear momentum or simply
momentum of a particle is defined as product of mass with velocity. It is
denoted as ![]() . Momentum is
also a vector quantity.
. Momentum is
also a vector quantity.
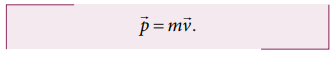
The direction of momentum is also in
the direction of velocity, and the magnitude of momentum is equal to product of
mass and speed of the particle.
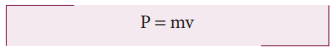
In component form the momentum can
be written as
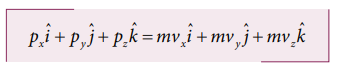
Here px = x
component of momentum and is equal to mvx
py = y component
of momentum and is equal to mvy
pz
= z component of
momentum and is equal to mvz
The momentum of the particle plays a
very important role in Newton’s laws. The physical significance of momentum can
be well understood by the following example.
Consider a butterfly and a stone,
both moving towards you with the same velocity 5 m s-1.
If both hit your body, the effects will not be the same. The effects not only
depend upon the velocity, but also on the mass. The stone has greater mass
compared to the butterfly. The momentum of the stone is thus greater than the
momentum of the butterfly. It is the momentum which plays a major role in
explaining the ‘state’ of motion of the object.
The unit of the momentum is kg m s-1
Solved Example Problems for Average speed
Example 2.20
Consider an object travelling in a semi-circular path from point O to point P in 5 second, as is shown in the Figure. Calculate the average velocity and average speed.
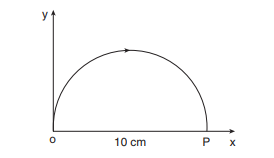
Solution
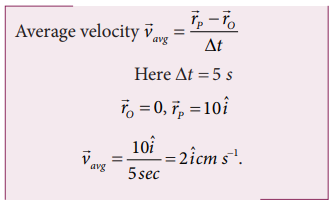
The average velocity is in the positive x direction.
The average speed = total path length / time taken (the path is semi-circular)

Note that the average speed is greater than the magnitude of the average velocity.
Solved Example Problems Instantaneous velocity or velocity
Example 2.21
The position vector of a particle is given 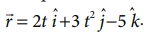
Calculate the velocity and speed of the particle at any instant t
Calculate the velocity and speed of the particle at time t = 2 s
Solution
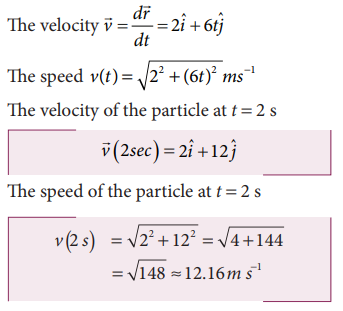
Note that the particle has velocity components along x and y direction. Along the z direction the position has constant value (-5) which is independent of time. Hence there is no z-component for the velocity.
Example 2.22
The velocity of three particles A, B, C are given below. Which particle travels at the greatest speed?
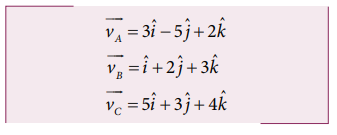
Solution
We know that speed is the magnitude of the velocity vector. Hence,

The particle C has the greatest speed.
Example 2.23
Two cars are travelling with respective velocities ![]() =10ms-1 along east and
=10ms-1 along east and ![]() =10ms-1 along west What are the speeds of the cars?
=10ms-1 along west What are the speeds of the cars?
Solution
Both cars have the same magnitude of velocity. This implies that both cars travel at the same speed even though they have velocities in different directions. Speed will not give the direction of motion.

Solved Example Problems Momentum
Example 2.24
Consider two masses of 10 g and 1 kg moving with the same speed 10 m s-1. Calculate the magnitude of the momentum.
Solution
We use p = mv
For the mass of 10 g, m = 0.01 kg

Thus even though both the masses have the same speed, the momentum of the heavier mass is 100 times greater than that of the lighter mass.
Related Topics