Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Patients With Hematologic Disorders
Nursing Process: The Patient With Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
NURSING
PROCESS: THE PATIENT WITH DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION (DIC)
Assessment
Nurses
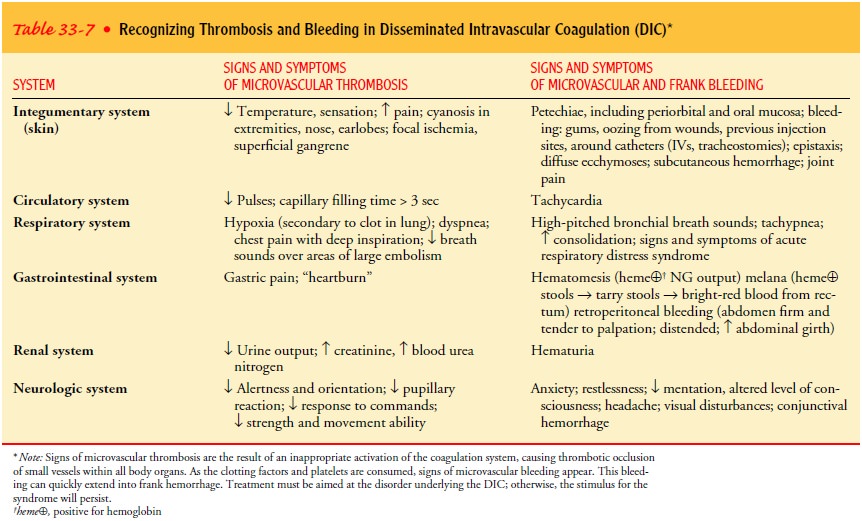
need to be aware of patients who are at risk for DIC. Sep-sis and acute
promyelocytic leukemia are the most common causes of DIC. Patients need to be
assessed thoroughly and fre-quently for signs and symptoms of thrombi and
bleeding and monitored for any progression of these signs (see Table 33-7).
Diagnosis
NURSING DIAGNOSES
Based
on the assessment data, major nursing diagnoses for the pa-tient with DIC may
include the following:
•
Risk for deficient fluid volume related to bleeding
•
Risk for impaired skin integrity related to
ischemia or bleeding
•
Potential for excess fluid volume related to
excessive blood/ factor component replacement
•
Ineffective tissue perfusion related to
microthrombi
• Anxiety and fear of the unknown and possible death
COLLABORATIVE PROBLEMS/POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS
Collaborative
problems include the clinical conditions that pre-cipitated the DIC. Based on
the assessment data, potential com-plications may include:
•
Renal failure
•
Gangrene
•
Pulmonary embolism or hemorrhage
•
Altered level of consciousness
•
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
•
Stroke
Planning and Goals
Major
patient goals include maintenance of hemodynamic status, maintenance of intact
skin and oral mucosa, maintenance of fluid balance, maintenance of tissue perfusion,
en-hanced coping, and absence of complications (see Plan of Nurs-ing Care).
Nursing Interventions
See
Plan of Nursing Care: The Patient with Disseminated In-travascular Coagulation.
MONITORING AND MANAGING POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS
Despite aggressive measures, the lack of renal perfusion may result in acute renal failure, sometimes necessitating dialysis. Placement of a large-bore dialysis catheter is extremely hazardous in this pa-tient population and should be accompanied by adequate platelet and plasma transfusions.
Evaluation
See
the Plan of Nursing Care for evaluation and expected out-comes for the patient
with DIC.
Related Topics