Atomic and Nuclear Physics | Physics - Summary, Concept Map | 12th Physics : UNIT 9 : Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 9 : Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Summary, Concept Map
SUMMARY
• A device used to
study the conduction of electricity through gases is known as gas discharge
tube
• Charge per unit
mass is known as specific charge or normalized charge, and it is independent of
gas used and also nature of electrodes used
• The minimum
distance between alpha particle and centre of the nucleus just before it gets
reflected back by 180º is defined as distance of closest approach r0
• The impact parameter
(b) (see Figure 8.12) is defined as the perpendicular distance between the
centre of the gold nucleus and the direction of velocity vector of alpha
particle when it is at a large distance.
• According to Bohr atom model,
angular momentum is quantized.
• The radius of the orbit in Bohr
atom model is rn = a0 n2/Z
• The radius of first orbit is a0 = ε0h2 /
πme2 = 0.529 Å also known
as Bohr radius
• The velocity of electron in nth
orbit is υn = 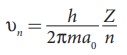
• The fine structure constant is α =
1/137 which is a dimensionless constant
• The total energy of electron in
the nth orbit is En
= 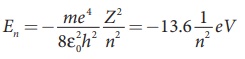
• The energy
required to excite an electron from the lower energy state to any higher energy
state is known as excitation energy and corresponding potential supplied is
known as excitation potential.
• The minimum
energy required to remove an electron from an atom which is in ground state is
known as ionization energy.
• The potential
difference through which an electron should be accelerated to get ionization
energy is known as ionization potential.
• The wavelength of
spectral lines of Lyman series lies in ultra-violet region
• The wavelength of
spectral lines of Balmer series lies in visible region while those of Paschen
and Brackett series lie in infra-red region
• The nucleus of element X having
atomic number Z and mass number A is represented by AZX
• The radius of nucleus (Z > 10) of mass number A is given by R = R0A1/3
where R0 = 1.2 F
• The density of nucleus ρ = 2.3×1017
kg m−3
• If M, mp and mn
are masses of a nucleus ( AZX ), proton and neutron respectively , then the mass defect is ∆m = (Zmp
+ Nmn ) - M
• The binding energy of nucleus B.E
= (Zmp + Nmn - M )c2
• The binding energy per nucleon is maximum for iron which is 8.8 MeV.
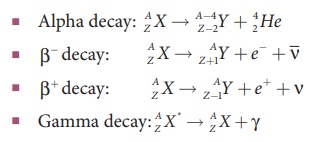
• Law of radioactive decay: N = N0
e-λt
• In general, after n half lives, the number of nuclei
undecayed is N = ( 1/2)n N0
• The relation between half-life and
decay constant T1/2 = ln2
/ λ
• If a heavier nucleus decays into
lighter nuclei, it is called nuclear fission
• If two lighter nuclei fuse to
heavier nuclei, it is called nuclear fusion
• In nuclear reactors, the nuclear chain reaction is controlled. In stars, the energy generation is through nuclear fusion.
CONCEPT MAP
Related Topics