Physics - Electric Discharge Through Gases | 12th Physics : UNIT 9 : Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 9 : Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Electric Discharge Through Gases
ELECTRIC DISCHARGE THROUGH GASES
Gases at normal atmospheric pressure
are poor conductors of electricity because they do not have free electrons for
conduction.
But by special arrangement, one can
make a gas to conduct electricity.
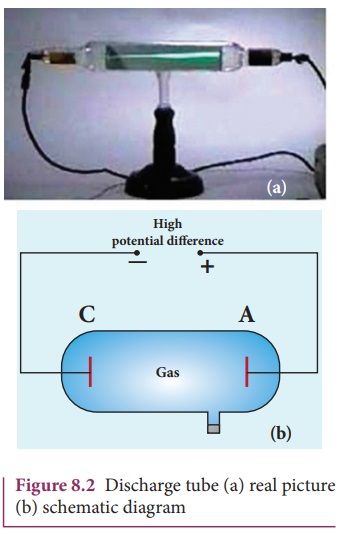
A simple and convenient device used
to study the conduction of electricity through gases is known as gas discharge
tube. The arrangement of discharge tube is shown in Figure 8.2. It consists of
a long closed glass tube (of length nearly 50 cm and diameter of 4 cm) inside of
which the gas in pure form is filled usually. The small opening in the tube is
connected to a high vacuum pump and a low-pressure gauge. This tube is fitted
with two metallic plates known as electrodes which are connected to secondary
of an induction coil. The electrode connected to positive of secondary is known
as anode and the electrode to the negative of the secondary is cathode. The
potential of secondary is maintained about 50 kV.
Suppose the pressure of the gas in
discharge tube is reduced to around 110 mm of Hg using vacuum pump, it is
observed that no discharge takes place. When the pressure is kept near 100 mm
of Hg, the discharge of electricity through the tube takes place. Consequently,
irregular streaks of light appear and also crackling sound is produced. When
the pressure is reduced to the order of 10 mm of Hg, a luminous column known as
positive column is formed from anode to cathode.
When the pressure reaches to around 0.01 mm of Hg, positive column disappears. At this time, a
dark space is formed between anode and cathode which is often called Crooke’s
dark space and the walls of the tube appear with green colour. At this stage,
some invisible rays emanate from cathode called cathode rays, which are later
found be a beam of electrons.
Properties of cathode rays
(1) Cathode rays possess energy and
momentum and travel in a straight line with high speed of the order of 107m s-1.
It can be deflected by application of electric and magnetic fields. The
direction of deflection indicates that they are negatively charged particles.
(2) When the cathode rays are
allowed to fall on matter, they produce heat. They affect the photographic
plates and also produce fluorescence when they fall on certain crystals and
minerals.
(3) When the cathode rays fall on a
material of high atomic weight, x-rays are produced.
(4) Cathode rays ionize the gas through
which they pass.
(5) The speed of cathode rays is up
to (1/10)th of the speed of light.
Related Topics