Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 9 : Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Nuclear Force
NUCLEAR FORCE
Nucleus contains protons and
neutrons. From electrostatics, we learnt that like charges repel each other. In
the nucleus, the protons are separated by a distance of about a few Fermi (10-15
m ), they must exert on each other a
very strong repulsive force. For example, the electrostatic repulsive force
between two protons separated by a distance 10-15 m
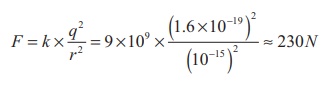
The acceleration experienced by a
proton due to the force of 230 N is
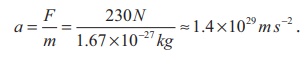
This is nearly 1028 times
greater than the acceleration due to gravity. So if the protons in the nucleus
experience only the electrostatic force, then the nucleus would fly apart in an
instant. Then how protons are held together in nucleus?
From this observation, it was
concluded that there must be a strong attractive force between protons to
overcome the repulsive Coulomb’s force. This attractive force which holds the
nucleus together is called strong nuclear force. The properties of strong
nuclear force were understood through various experiments carried out between
1930s and 1950s. A few properties of strong nuclear force are
(i) The strong nuclear force is of
very short range, acting only up to a distance of a few Fermi. But inside the
nucleus, the repulsive Coulomb force or attractive gravitational forces between
two protons are much weaker than the strong nuclear force between two protons.
Similarly, the gravitational force between two neutrons is also much weaker
than strong nuclear force between the neutrons. So nuclear force is the
strongest force in nature.
(ii) The strong nuclear force is
attractive and acts with an equal strength between proton-proton,
proton-neutron, and neutron ‚Äď neutron.
(iii) Strong nuclear force does not
act on the electrons. So it does not alter the chemical properties of the atom.
Related Topics