Nuclear Physics - Binding energy curve | 12th Physics : UNIT 9 : Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 9 : Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Binding energy curve
Binding
energy curve
In the previous section, the origin of the binding energy is
discussed. Now we can find the average binding energy per nucleon ![]() . It is given by
. It is given by
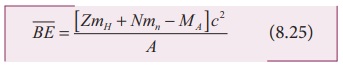
The average binding energy per
nucleon is the energy required to separate single
nucleon from the particular nucleus. ![]() is plotted against A of all known
nuclei. It gives a curve as seen in Figure 8.24.
is plotted against A of all known
nuclei. It gives a curve as seen in Figure 8.24.
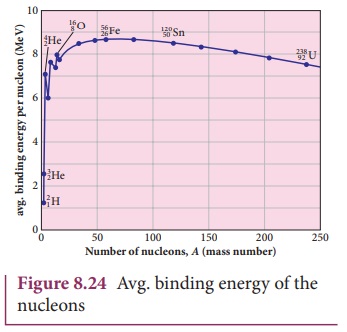
Important inferences from of the average binding energy curve:
(1) The value of ![]() rises as the mass number increases until it reaches a maximum value of 8.8
MeV for A = 56 (iron) and then it slowly decreases.
rises as the mass number increases until it reaches a maximum value of 8.8
MeV for A = 56 (iron) and then it slowly decreases.
(2) The average binding energy per nucleon is about 8.5 MeV for
nuclei having mass number between A= 40 and 120. These elements are
comparatively more stable and not radioactive.
(3) For higher mass numbers, the curve reduces slowly and ![]() for uranium is about 7.6 MeV. They
are unstable and radioactive.
for uranium is about 7.6 MeV. They
are unstable and radioactive.
From Figure 8.24, if two light nuclei with A<28 combine with
a nucleus with A<56, the binding energy per nucleon is more for final
nucleus than initial nuclei. Thus, if the lighter elements combine to produce a
nucleus of medium value A, a large amount of energy will be released. This is
the basis of nuclear fusion and is the principle of the hydrogen bomb.
(4) If a nucleus of heavy element is
split (fission) into two or more nuclei of medium value A, the energy released
would again be large. The atom bomb is based on this principle and huge energy
of atom bombs comes from this fission when it is uncontrolled. Fission is
explained in the section 8.7.
EXAMPLE 8.10
Compute the binding energy per
nucleon of 42He nucleus.
Solution
From example 8.9, we found that the ![]() of
42He =28 Mev
of
42He =28 Mev
Binding energy per nucleon = ![]() = 28 MeV/4 = 7 MeV.
= 28 MeV/4 = 7 MeV.
Related Topics