Laws of Motion | Physics - Short Questions and Answer | 11th Physics : UNIT 3 : Laws of Motion
Chapter: 11th Physics : UNIT 3 : Laws of Motion
Short Questions and Answer
Laws of Motion - Physics
Short Answer Questions
1. Explain the concept of inertia. Write two examples each for inertia of motion, inertia of rest and inertia of direction.
Inertia:-
This
inability of objects to move on its own or change its state of
motion is called inertia.
Inertia
of rest:- The inability of an object to change its state of rest is
called inertia of rest.
Example:
1.
When stationary bus starts to move the passengers experience a sudden backward
push. Due to inertia, the body will try to continue in the state of rest, while
the bus moves forward.
2.
A book lying on the table will remain at rest, until it is moved by some
external agencies.
Inertia
of motion: The inability of an object to change its state of
uniform speed on its own is called inertia of motion.
Example:
1.
When the bus is in motion and if the brake is applied suddenly, passengers move
forward and hit against the front seat. As the bus stop, the body continue to
move forward due to property of inertia.
2.
An athlete running in a race will continue to run even after reaching the
finishing point.
Inertia
of direction: The inability of an object to change its
direction of motion on its own is called inertia of direction.
Example:
1.
When a stone attached to a string is in whirling motion, and if the string is
cut suddenly the stone will not continue to move in circular motion but moves
tangential to the circle.
2.
When a bus moving along straight line takes a turn to the right, the passengers
are thrown towards left.
2. State Newton’s second law.
The
force acting on an object is equal to the rate of change of its momentum
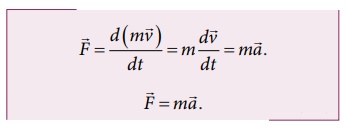
3. Define one newton.
One
newton is defined as the force which acts on 1 kg of mass to give an
acceleration 1ms-2 in the direction of the force.
4. Show that impulse is the change of momentum.
If
a force (F) acts on the object in a very short interval of time (Δt), from
Newton’s second law in magnitude form
F
dt = dp ………..(1)
Integrating
the above equation
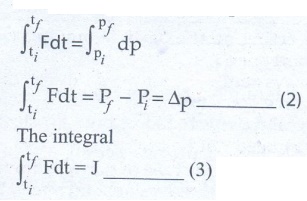
is
called impulse from eqn. 2 and 3
J
= Δp
So,
Impulse is equal to change in momentum of the object.
5. Using free body diagram, show that it is easy to pull an object than to push it.
It
is easier to pull an object than to push to make it move. When a body is pushed
at an arbitrary angle θ (0 to π/2 ), the applied force F can be resolved into
two components as F sinθ parallel to the surface and F cosθ perpendicular to
the surface.
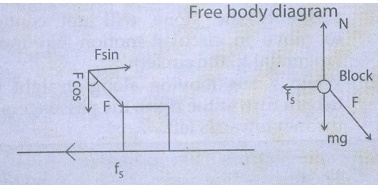
The
total downward force mg+Fcosθ act on the body which is implies that normal
force acting on the body increases.
Since
there is no acceleration along the vertical direction, the normal force N is
given by
Npush
= mg + Fcosθ …………… (1)
As
a result the maximum static friction also increase and is give by the equation.
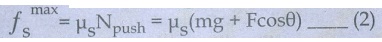
ƒsmax
= μsNpush = μs (mg + Fcosθ) ………. (2)
a
greater force a needs to be applied to push the object into motion.
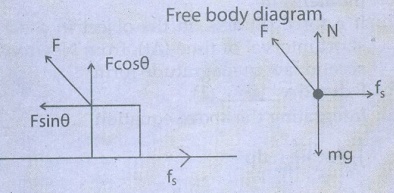
From
diagram Npull = mg – Fcosθ
…………. (3)
The
Total downward force mg - Fcosθ.
ƒsmax
= μsNpull = μs (mg − Fcosθ) ………. (4)
Hence
from (2) and (4) shows that the normal force. Npull is less than Npush
and it is easier to pull an object than to push to make it move.
6. Explain various types of friction. Suggest a few methods to reduce friction.
Types
of friction is
1.
Static friction
2.
Kinetic friction
3.
Limiting friction
Static
friction : Static friction is the force which always opposes the
movement of the object from rest.
It
can take values from zero to μsN. If an external force greater than μsN
then object begins to move.
Kinetic
friction : The force of friction which comes into effect, when a body is
in motion with constant velocity over the surface of another body is called
kinetic friction (or) dynamic friction.
Limiting
friction: The maximum force of static friction (ƒsmax)
which comes into effect when a body just starts moving over the surface of another
body is called limiting friction (ie) ƒs ≤ƒsmax
Method
of reducing friction :
1.
To reduce kinetic friction in Heavy machines and industries lubricants like
oil, grease etc., are used.
2.
To reduce kinetic friction in machines ball bearings are used
3.
To reduce friction by making the surfaces in contact are made highly polished
and smooth.
7. What is the meaning by ‘pseudo force’?
Pseudo
force means 'centrifugal force' such a force which does not really act on
particles but appears due to acceleration of the frame is called pseudo force.
8. State the empirical laws of static and kinetic friction.
Static
friction 0 ≤ fsmax (or)
0 ≤ fs ≤
μsN
Kinetic
friction fK ≤ fsmax
(ie)
μk < μs
9. State Newton’s third law.
●
Newton’s third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite
reaction.
●
Here action and reaction pair of forces do not act on the same body but on two
different bodies.
●
It is valid in both inertial and non inertial frames.
10. What are inertial frames?
A
frame of reference in which Newton's first law of motion holds good is called
an Gravity frame of reference.
In
this frame, a body remains at rest or in continuous motion unless acted upon by
external force.
11. Under what condition will a car skid on a leveled circular road?
mv2 /r >
μs mg (or) μs < v2 / rg
If
the static friction is not able to provide enough centripetal force to turn,
the vehicle will start to skid.
Related Topics