Physics - Semiconductor Electronics | 12th Physics : UNIT 10a : Semiconductor Electronics
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 10a : Semiconductor Electronics
Semiconductor Electronics
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS
Electronics is clearly the
winner of the day ŌĆō John Ford.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
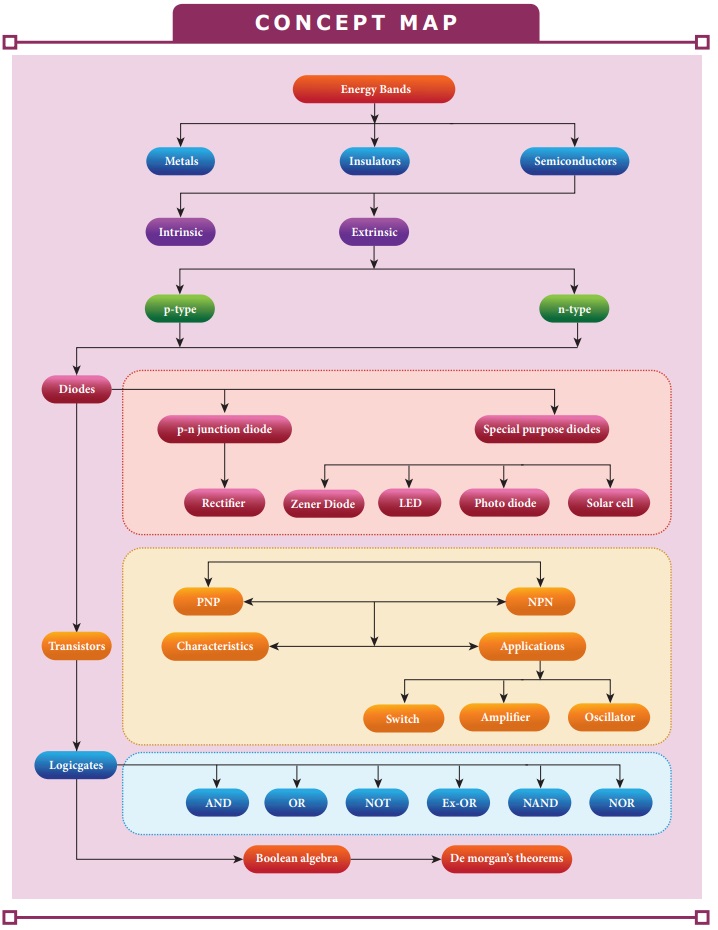
In this unit, the students are exposed to,
ŌĆó Energy band
diagram in semiconductors
ŌĆó Types of
semiconductors
ŌĆó Formation of p-n
junction diode and its V-I characteristics
ŌĆó Rectification
process
ŌĆó Special purpose
diodes
ŌĆó Transistors and
their immediate applications
ŌĆó Digital and
analog signals
ŌĆó Logic gates
ŌĆó Boolean algebra
ŌĆó De MorganŌĆÖs theorem
INTRODUCTION
Electronics has become a part of our
daily life. All gadgets like mobile phones, computers, televisions, music
systems etc work on the electronic principles. Electronic circuits are used to
perform various operations in devices like air conditioners, microwave oven,
dish washers and washing machines. Besides this, its applications are
widespread in all fields like communication systems, medical diagnosis and
treatments and even handling money through ATMs.
Evolution of Electronics:
The history of electronics began
with the invention of vacuum diode by J.A. Fleming in 1897. This was followed
by a vacuum triode implemented by Lee De Forest to control electrical signals.
This led to the introduction of tetrode and pentode tubes.
Subsequently, the transistor era
began with the invention of bipolar junction transistor by Bardeen, Brattain
and Shockley in 1948 for which Nobel prize was awarded in 1956. The emergence
of Germanium and Silicon semiconductor materials made this transistor gain popularity,
in turn its application in different electronic circuits.
The following years witnessed the
invention of the integrated circuits (ICs) that helped to integrate the entire
electronic circuit on a single chip which is small in size and cost-effective.
Since 1958 ICs capable of holding several thousand electronic components on a
single chip such as small- scale, medium-scale, large-scale, and very- large
scale integration started coming into existence. Digital integrated circuits
became another robust IC development that enhanced the architecture of
computers.All these radical changes led to the introduction of microprocessor
in 1969 by Intel.
The electronics revolution, in due
course of time, accelerated the computer revolution. Now the world is on its
way towards small particles of nano-size, far too small to see. This helps in
the miniaturization to an unimaginable size. A room-size computer during its
invention has now emerged as a laptop, palmtop, iPad, etc. In the recent past,
IBM revealed the smallest computer whose size is comparable with the tip of the
rice grain, measuring just 0.33 mm on each side.
Electronics is the branch of physics incorporated with technology
towards the design of circuits using transistors and microchips. It depicts the
behaviour and movement of electrons and holes in a semiconductor, electrons and
ions in vacuum, or gas. Electronics deals with electrical circuits that involve
active components such as transistors, diodes, integrated circuits, and
sensors, associated with the passive components like resistors, inductors,
capacitors, and transformers.
This chapter deals with
semiconductor devices like p-n junction diodes, bipolar junction transistors
and logic circuits.
Passive Components: components that cannot
generate power in a circuit. Active components: components that can generate
power in a circuit.

The worldŌĆÖs first computer ŌĆśENIACŌĆÖ
was invented by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly at the University of
Pennsylvania. The construction work started in 1943 and got over in 1946. It
occupied an area of around 1800 square feet. It had 18,000 vacuum tubes and it
weighed around 50 tons.
Related Topics