Bipolar Junction Transistor [BJT] - Transistor as a switch | 12th Physics : UNIT 10a : Semiconductor Electronics
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 10a : Semiconductor Electronics
Transistor as a switch
Transistor as a switch
The transistor in saturation and
cut-off regions functions like an electronic switch that helps to turn ON or
OFF a given circuit by a small control signal. The circuit is shown in Figure
9.34.
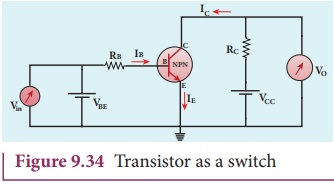
• Presence of dc source at the input (saturation region):
When a high input voltage (Vin = +5V ) is applied, the base current (IB) increases and in
turn increases the collector current. The transistor will move into the
saturation region (turned ON). The increase in collector current (IC)
increases the voltage drop across RC
, thereby lowering the output voltage, close to zero. The transistor acts like a closed switch and is equivalent to ON condition.
• Absence of dc source at the
input (cut-off region):
A low input voltage (Vin = 0V ), decreases the base current (IB) and in turn
decreases the collector current (IC). The transistor will move into
the cut-off region (turned OFF). The decrease in collector current (IC)
decreases the drop across RC ,
thereby increasing the output voltage, close to +5 V. The transistor acts as an
open switch which is considered as the OFF condition.
It is manifested that, a high input gives
a low output and a low input gives a high output. In addition, we can say that
the output voltage is opposite to the applied input voltage. Therefore, a
transistor can be used as an inverter (NOT gate) in computer logic circuitry.
Related Topics