with diagram - Ultrastructure of a Bacterial cell | 11th Botany : Chapter 1 : Living World
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 1 : Living World
Ultrastructure of a Bacterial cell
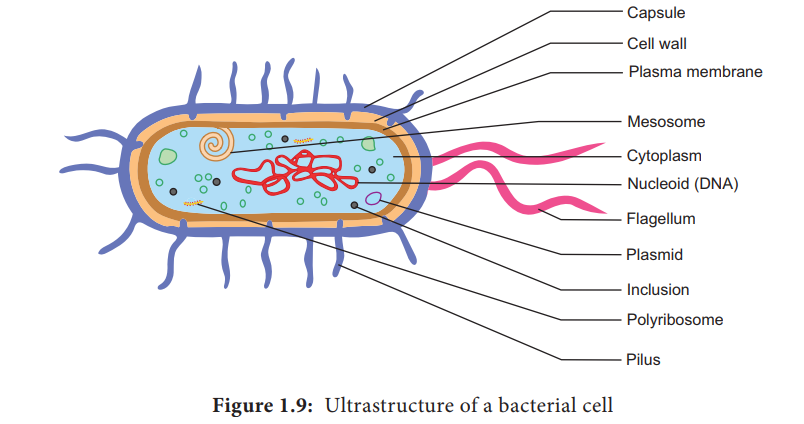
Ultrastructure of a Bacterial cell
The bacterial cell reveals three layers (i)
Capsule/Glycocalyx (ii) Cell wall and (iii) Cytoplasm (Figure 1.9)
Capsule/Glycocalyx
Some bacteria are surrounded by a gelatinous
substance which is composed of polysaccharides or polypeptide or both. A thick
layer of glycocalyx bound tightly to
the cell wall is called capsule. It
protects cell from desiccation and antibiotics. The sticky nature helps them to
attach to substrates like plant root surfaces, Human teeth and tissues. It
helps to retain the nutrients in bacterial cell.
Cell wall
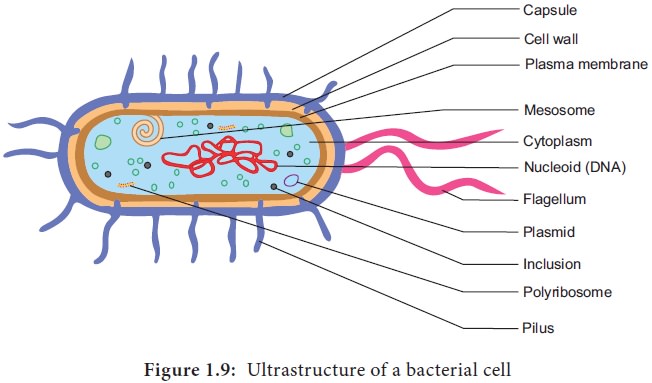
Plasma membrane
The plasma membrane is made up of lipoprotein. It
controls the entry and exit of small molecules and ions. The enzymes involved
in the oxidation of metabolites (i.e., the respiratory chain) as well as the
photosystems used in photosynthesis are present in the plasma membrane.
Cytoplasm
![]()
![]()
![]()
Cytoplasm is thick and semitransparent. It contains
ribosomes and other cell inclusions. Cytoplasmic inclusions like glycogen,
poly-β-hydroxybutyrate granules, sulphur granules and gas vesicles are present.
Bacterial chromosome
The bacterial chromosome is a single circular DNA
molecule, tightly coiled and is not enclosed in a membrane as in Eukaryotes.
This genetic material is called Nucleoid
or Genophore. It is amazing to
note that the DNA of E.coli which
measures about 1mm long when uncoiled, contains all the genetic information of
the organism. The DNA is not bound to histone
proteins. The single chromosome or
the DNA molecule is circular and at one point it is attached to the plasma
membrane and it is believed that this attachment may help in the separation of
two chromosomes after DNA replication.
Plasmid
Plasmids are extra chromosomal double stranded,
circular, self-replicating, autonomous elements. They contain genes for
fertility, antibiotic resistant and heavy metals. It also help in the
production of bacteriocins and toxins which are not found in bacterial
chromosome. The size of a plasmid varies from 1 to 500 kb usually plasmids
contribute to about 0.5 to 5.0% of the total DNA of bacteria. The number of
plasmids per cell varies. Plasmids are classified into different types based on
the function. Some of them are F (Fertility) factor, R (Resistance) plasmids,
Col (Colicin) plasmids, Ri (Root inducing) plasmids and Ti (Tumour inducing)
plasmids.
Mesosomes
These are localized infoldings of plasma membrane
produced into the cell in the form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae. They are
clumped and folded together to maximize their surface area and helps in
respiration and in binary fission.
Polysomes / Polyribosomes
The ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis.
The number of ribosome per cell varies from 10,000 to 15,000. The ribosomes are
70S type and consists of two subunits (50S and 30S). The ribosomes are held
together by mRNA and form polyribosomes or polysomes.
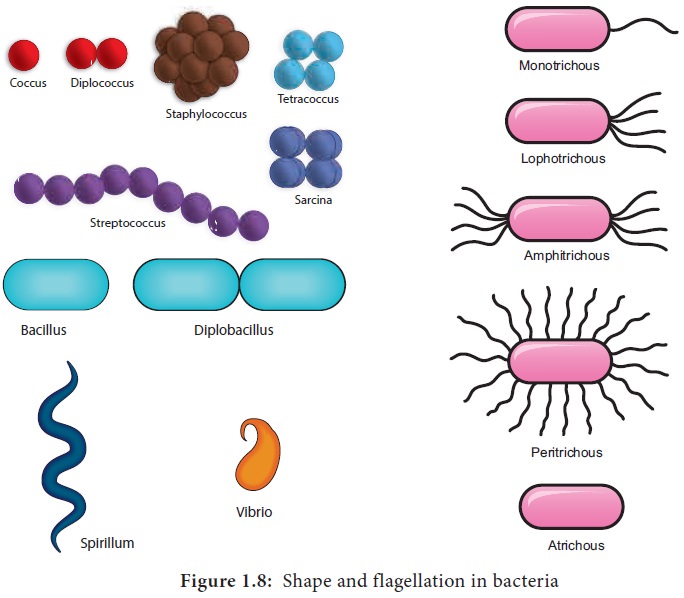
Flagella
Certain motile bacteria have numerous thin hair
like processes of variable length emerge from the cell wall called flagella. It
is 20–30 μm in diameter and 15 μm in length. The flagella of Eukaryotic cells
contain 9+2 microtubles but each flagellum in bacteria is made up of a single
fibril. Flagella are used for locomotion. Based on the number and position of
flagella there are different types of bacteria (Figure 1.8)
Fimbriae or Pili
Related Topics