Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 1 : Living World
Methods of Reproduction in Fungi : Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
Methods of
Reproduction in Fungi
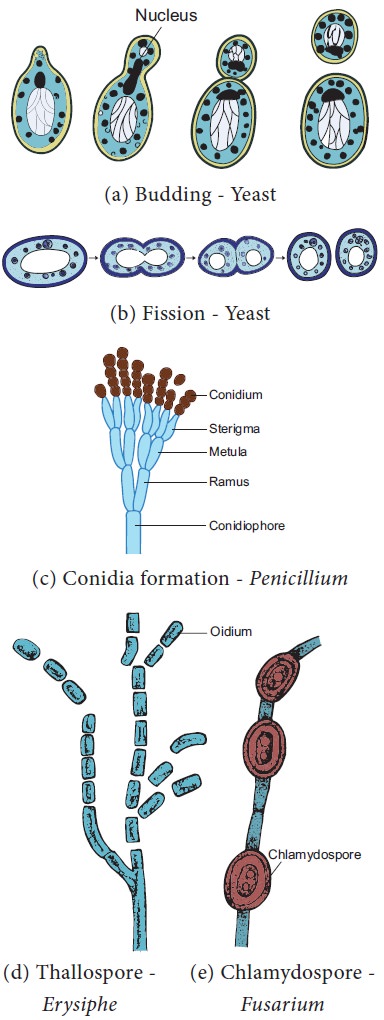
Asexual Reproduction
1. Zoospores:
They are flagellate structures produced in zoosporangia (Example: Chytrids)
2. Conidia:
The spores produced on condiophores (Example:
Aspergillus)
3. Oidia/Thallospores/Arthrospores:
The hypha divide and develop in to spores called oidia (Example: Erysiphe).
4. Fission:
The vegetative cell divide into 2 daughter cells. (Example: Schizosaccharomyces-yeast).
5.
Budding: A small outgrowth is developed on parent
cell, which gets detached and become independent. (Example: Saccharomyces-yeast)
6. Chlamydospore:
Thick walled resting spores are called chlamydospores (Example: Fusarium).
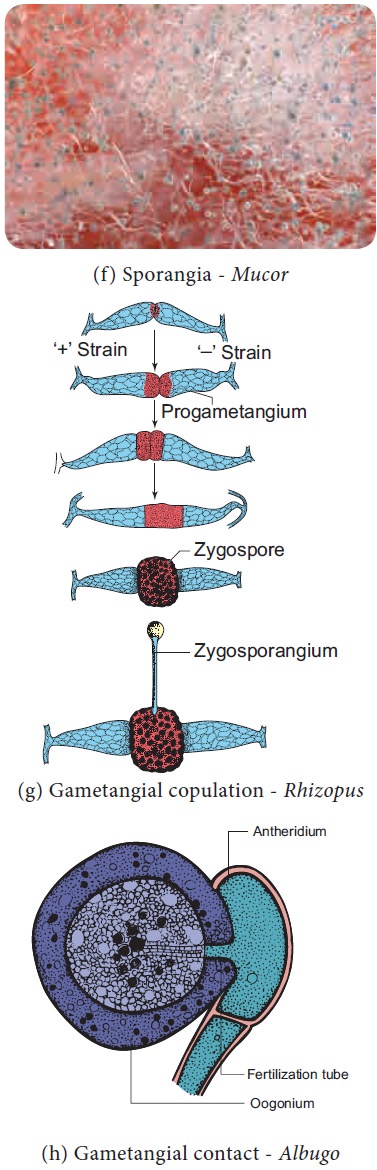
Sexual Reproduction
1.Planogametic
copulation: Fusion of motile gamete is called planogametic copulation. a.
Isogamy – Fusion of morphologically and physiologicall similar gametes.
(Example: Synchytrium). b. Anisogamy
– Fusion of morphologically or
physiologically dissimilar gametes (Example: Allomyces). c. Oogamy – Fusion of both morphologi-cally and
physiologically dissimilar gam-etes. (Example: Monoblepharis)
2.
Gametangial contact: During sexual reproduction a
contact is established between antheridium and Oogonium (Example: Albugo)
3. Gametangial copulation: Fusion of gametangia to
form zygospore (Example: Mucor, Rhizopus).
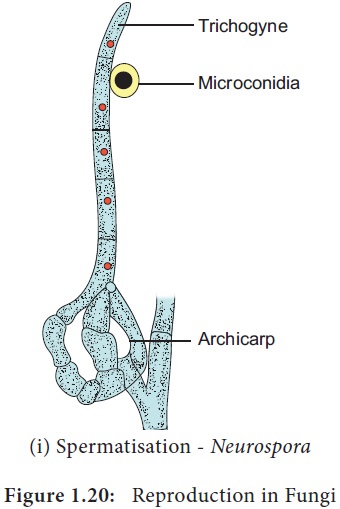
4. Spermatization:
In this method a un-inucleate pycniospore/microconidium is transferred to
receptive hyphal cell (Example: Puccinia/Neurospora)
5. Somatogamy:
Fusion of two somatic cells of the hyphae (Example: Agaricus)
![]()
![]()
![]()
Related Topics