Viruses | Botany - Multiplication or Life Cycle of Phages | 11th Botany : Chapter 1 : Living World
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 1 : Living World
Multiplication or Life Cycle of Phages
Multiplication or Life Cycle of Phages
Phages multiply through two different types of life
cycle. a. Lytic or Virulent cycle b. Lysogenic or Avirulent life cycle
a. Lytic Cycle
During lytic cycle of phage, disintegration of host
bacterial cell occurs and the progeny virions are released (Figure 1.5a). The
steps involved in the lytic cycle are as follows:
(i) Adsorption
Phage (T4) particles interact with cell
wall of host (E. coli). The phage
tail makes contact between the two, and tail fibres recognize the specific
receptor sites present on bacterial cell surface. The lipopolysaccharides of
tail fibres act as receptor in phages. The process involving the recognition of
phage to bacterium is called landing.
Once the contact is established between tail fibres and bacterial cell, tail
fibres bend to anchor the pins and base plate to the cell surface. This step is
called pinning.
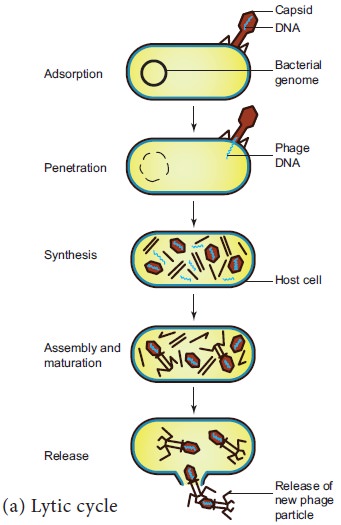
(ii) Penetration
The penetration process involves mechani-cal and
enzymatic digestion of the cell wall of the host. At the recognition site phage
digests certain cell wall structure by viral enzyme (lysozyme). After pinning
the tail sheath contracts (using ATP) and appears shorter and thicker. After
contraction of the base plate enlarges through which DNA is injected into the
cell wall without using metabolic energy. The step involving injection of DNA
particle alone into the bacterial cell is called Transfection. The empty protein coat leaving outside the cell is
known as ‘ghost’.
(iii) Synthesis
This step involves the degradation of bacterial
chromosome, protein synthesis and DNA replication. The phage nucleic acid takes
over the host biosynthetic machinery. Host DNA gets inactivated and breaks
down. Phage DNA suppresses the synthesis of bacterial protein and directs the
metabolism of the cell to synthesis the proteins of the phage particles and
simultaneously replication of Phage DNA also takes place.
(iv) Assembly and Maturation
The DNA of the phage and protein coat are synthesized separately and are assembled to form phage particles. The process of assembling the phage particles is known as maturation. After 20 minutes of infection about 300 new phages are assembled.
![]()
![]()
![]()
(v) Release
The phage particle gets accumulated inside the host
cell and are released by the lysis of host cell wall.
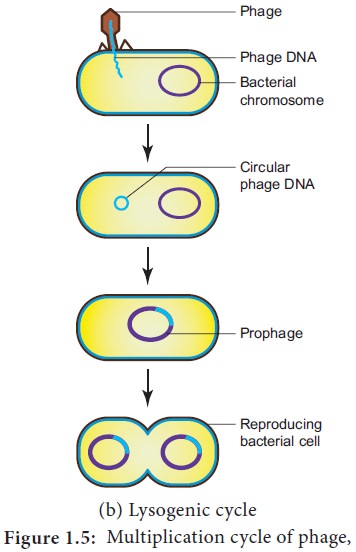
b. Lysogenic Cycle
In the lysogenic cycle the phage DNA gets
integrated into host DNA and gets multiplied along with nucleic acid of the
host. No independent viral particle is formed (Figure 1.5b).
As soon as the phage injects its linear DNA into
the host cell, it becomes circular and integrates into the bacterial chromosome
by recombination. The integrated phage DNA is now called prophage. The activity of the prophage gene is repressed by two repressor proteins which are synthesized
by phage genes. This checks the synthesis of new phages within the host cell.
However, each time the bacterial cell divides, the prophage multiplies along
with the bacterial chromosome. On exposure to UV radiation and chemicals the
excision of phage DNA may occur and results in lytic cycle.

Virion is an
intact infective virus particle
which is non-replicating outside a host cell.
Viroid is a
circular molecule of ssRNA without a
capsid and was discovered by T.O.Diener in the year 1971. The RNA of viroid has
low molecular weight. Viroids cause citrus exocortis and potato spindle tuber
disease in plants.
Virusoids were discovered
by J.W.Randles and Co-workers in 1981.
They are the small circular RNAs which are similar
to viroids but they are always linked with larger molecules of the viral RNA.
Prions were
discovered by Stanley B. Prusiner in
the year 1982 and are pro-teinaceous infectious particles. They are the
causative agents for about a dozen fatal degenerative disorders of the
central nervous system of humans and other animals . For example Creutzfeldt – Jakob
Disease (CJD), Bovine Spongiform En-cephalopathy (BSE) – commonly known as mad
cow disease and scrapie disease of sheep.
Viruses infecting blue green algae are called Cyanophages and are first reported by
Safferman and Morris in the year 1963(Example LPP1 - Lyngbya, Plectonema and Phormidium). Similarly, Hollings(1962)
reported viruses infecting cultivated Mushrooms and causing die back disease.
The viruses attacking fungi are called Mycoviruses
or Mycophages.
Related Topics