Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 1 : Living World
Agaricus - Fungi
Agaricus
Class - Basidiomycetes
Order - Agaricales
Family - Agaricaceae
Genus - Agaricus
It is a saprophytic fungus found on wood logs, manure
piles, fresh litter, pastures etc., The fruit bodies are the visible part of
the fungi. They are found in rings in some species like Agaricus arvensis, Agaricus
tabularis and hence popularly called
‘Fairy rings”. Agaricus campestris is
the most common ‘field mushroom’.
Vegetative structure
The thallus is made up of branched structures
called hyphae. A large number of hyphae constitute the mycelium.
Three types of mycelia are seen namely primary
mycelium, secondary mycelium and tertiary mycelium, The primary mycelium
develops from the germination of basidiospore. It is septate, uninucleate and
haploid. It is also called monokaryotic
mycelium. Fusion of two primary
mycelium of opposite strains give rise to secondary mycelium or dikaryotic mycelium. The dikaryotic mycelium develops into hyphal cords called Rhizomorphs,. and perennates the soil for a long period. The tertiary mycelium is found in the fruit
body called basidiocarp. Each cell
of the hyphae posssess a cell wall made up of chitin and cell organelles like
mitochondria, golgibodies, Endoplasmic reticulum etc., are also present.
Asexual reproduction.
Agaricus produces
chlamydospores during asexual
reproduction. During favourable condition the chlamydospores germinate and produce
mycelium.
Sexual reproduction
Agaricus reproduces
by sexual method but sex organs are
absent.Majority of the species are heterothallic. Agaricus bisporus is a homothallic species. The opposite strains of
mycelium fuse(somatogamy) and results in the formation of dikaryotic or
secondary mycelium. Karyogamy takes place in basidium and it is immediately
followed by meiosis giving rise to four haploid basidiospores. The
basidiospores are borne on sterigmata. The subterranean mycelial strands called
rhizomorphs posssess dense knots of dikaryotic hyphae. These knots develop into
Basidiocarps.
![]()
![]()
![]()
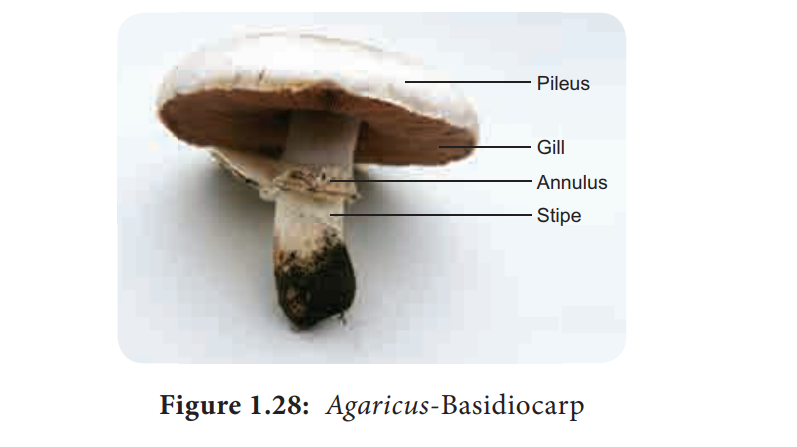
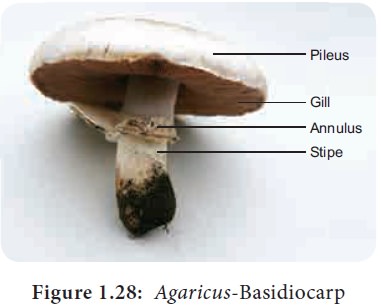
Basidiocarp
The mature basidiocarp is umbrella shaped and is divided into 3 parts namely stipe, pileus and gill. The stipe is thick, fleshy and cylindrical in structure. The upper part of the stipe possess a membranous structure called annulus. The upper convex surface is called Pileus which is white or cream in colour (Figure 1.28). The inner surface of pileus shows radially arranged gills or lamellae. The gills vary in length. On both the sides of the gills a fertile layer called hymenium is present. The stipe is hollow from the centre and the central part is made up of loosely arranged hyphae whereas the periphery is made up of compactly arranged hyphae forming pseudoparenchymatous tissue. The gill region is divided into 3 regions. The central part of gill between two hymenial layers is called Trama (Figure 1.29). The subhymenial layers have closely compact tissue . The hymenium is the fertile layer and possess club shaped basidia. The basidium is interspersed with sterile hyphae called paraphysis. Each basidium bears 4 basidiospores , of these two basidiospore belong to (+) strain and other two of them will be (–) strain. The basidiospores are borne on stalk like structures called Sterigmata. The basidiospore on germination produces the haploid primary mycelium.
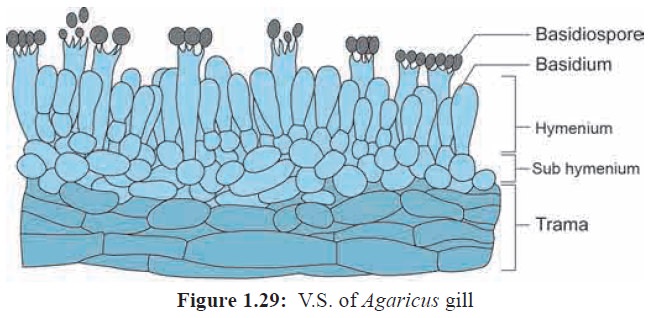
Thus the life cycle of Agaricus shows a very short diploid phase, haploid phase and a
prolonged dikaryotic phase (Figure 1.30).

Related Topics