Living World | Botany - Answer the following questions | 11th Botany : Chapter 1 : Living World
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 1 : Living World
Answer the following questions
Diversity of Living World
Living World
6. Differentiate Homoiomerous and Heteromerous lichens.
Homoiomerous
1.
Here algae cells evenly distributed in the thallus
Heteromerous
1.
Heteromerous-a distinct layer of alga and fungi present.
7. Write the distinguishing features of Monera.
Monera
include - I. Archaebacteria II. Eubacteria.
I. Archarbacteria - It is
primitive they are adapted to thrive in extreme environmental conditions
•
Hot springs
•
High salinity condition
•
Absence of oxygen
•
Low pH (high acidic condition)
•
Their cell membrane is made up of lipids like glycerol and isopropylethers so
resist high temperature and antibiotics.
II. Eubacteria - All
other bacterial types are kept under the category. Eg. Pseudomonas
a.
They are generally, prokaryotic, genetic material is called Nucleoid or
genophore or incipient nucleaus -Unicellulaar
b.
Cellwall is made up of
polysaccharide & protein
c.
Based on nutrition
i.
Heterotrophic - 1. Saprophylic - E.g.
Agrobacterium
2.
Parasitic - E.g. Vibrio cholera
ii.
Autotrophic - Have bacteria with Bacterio chlorophyll- e.g. chromatium.
d.
Motility - Motile or non motile
8. Why do farmers plant leguminous crops in crop rotations/mixed cropping?
Rhizobium-
Nitrogen fixing bacteria,
Living
in the root modules of leguminous plants has symbiotic association with it, fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert
it in to nitrates, there by increases the fertility of the soil.
Growing
legumes alternatively with paddy can help paddy to give high yield- This method
of growing paddy, alternatively with leguminous plants is known as crop rotation.
Mixed
cropping:
Amidst,
other crops. Leguminous crop are also raised as mixed crop - so that it
enriches the soil and increases the yield by fixing atmospheric nitrogen.
9. Briefly discuss on five Kingdom classification. Add a note on merits and demerits.
a.
Proposed by R.H. Whittaker (American
taxonomist)
b.
Criteria considered - cell structure,
Thallus Organization, Mode of Nutrition, Reproduction, and Phytogenitic Relations.
5
kingdom classifications include: -
a. Monera
b. Protista
c. Fungi
d. Plantae
e. Animalia
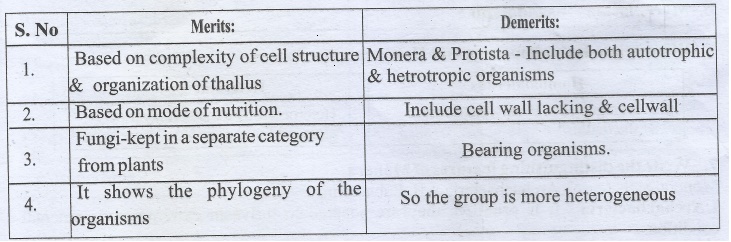
Merits:
1.
Based on complexity of cell structure & organization of thallus
2.
Based on mode of nutrition.
3.
Fungi-kept in a separate category from plants
4.
It shows the phylogeny of the organisms
Demerits:
1.
Monera & Protista - Include both autotrophic & hetrotropic organisms
2.
Include cell wall lacking & cellwall
3.
Bearing organisms.
4.
So the group is more heterogeneous
10. Give a general account on lichens.
a.
Definition: A symbolic association of
algae and Fungi helping each other & living together known as lichens.
b.
Partners: Algal partner known as Phycobiont & Fungal partner known
as Mycobiont
c.
Role of Algal partner - Autotrophic prepare food - give nutrition to fungal
partner also
d.
Role of fungal partner - gives protection- helps in fixing to the substratum by
rhizinae.
Classification:
1. Character of Asexual
reproduction
Phycobiont : Akinetes,
hormogonia, Aplanospore etc.
Mycobiont : fragmentation
soredia, and isidia
2. Character of Sexual
reproduction
Phycobiont : absent
Mycobiont : sexual reproduction by ascocarp & ascospores
1. Character : Habitat
Classification of lichens:
Corticolous
- growing on bark
Lichnicolous
- growing on wood
Saxicolous
- growing on rock
Terricolous
- growing on ground
Marine
- siliceous rock sea
Fresh
water - siliceous rocks (fresh water habitat).
2. Character : Morphology
of thallus
Classification of lichens:
Leprose
- distinct fungal layer absent
Crustose
- crust like
Foliose
- Leaf like
Fruticose-branched
pendulous shrub like
3. Character : On the
basis of distribution of algae cells
Classification of lichens:
Homoiomerous
- Algae cells evenly distributed
Heteromerous
- A distinct layer of Algae and Fungi present
4. Character : On the basis of fungal partner
Classification of lichens:
If
it is Asomycetes - Ascolichen
If it is basidiomycetes- Basidiolichen
Economic importance:
I.
Secretion of acids of lichens
1.
Oxalic acid Uses: Weathering of
rocks Pioneers in xerosere
2.
Usnic acid Uses: Antibacterial
II.
a. Pollution Indicators - Lichens
sensitive to air pollutants- (pollution indicators)
b.
Rocella montagnei - Produces a dye
used in litmus paper (acid base indicator)
c.
Cladonia rangiferina - Food for
animals in tundra regions
11. Explain the asexual reproduction in Rhizopus.
12. Mention the steps involved in the sexual reproduction of Rhizopus.
13. Write outline the life cycle of Agaricus.
14. What is Sterigma?
15. Name the types of mycelium found in Agaricus.
16. Differentiate oidium and Chlamydospore.
17. Name the fungal group which possess dolipore septum.
18. Mention the diseases caused by fungi in plants.
19. Give two examples for mycorrhizae forming fungi.
20. Differentiate Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria.
Related Topics