Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 7 : Thermodynamics
Thermodynamic processes and its Types
Thermodynamic processes
The method of operation which can bring about a change in the system is called thermodynamic process. Heating, cooling, expansion, compression, fusion, vaporization etc., are some examples of a thermodynamic process.
Types of processes:
A thermodynamic process can be carried out in different ways and under different conditions. The processes can be classified as follows:
Reversible process:
The process in which the system and surrounding can be restored to the initial state from the final state without producing any changes in the thermodynamic properties of the universe is called a reversible process. There are two important conditions for the reversible process to occur. Firstly, the process should occur infinitesimally slowly and secondly throughout the process, the system and surroundings must be in equilibrium with each other.
Irreversible Process:
The process in which the system and surrounding cannot be restored to the initial state from the final state is called an irreversible process. All the processes occurring in nature are irreversible processes. During the irreversible process the system and surroundings are not in equilibrium with each other.
Adiabatic process:
An adiabatic process is defined as one in which there is no exchange of heat between the system and surrounding during the process. Those processes in which no heat can flow into or out of the system are called adiabatic processes.
This condition is attained by thermally insulating the system. In an adiabatic process if work is done by the system its temperature decreases, if work is done on the system its temperature increases, because, the system cannot exchange heat with its surroundings.
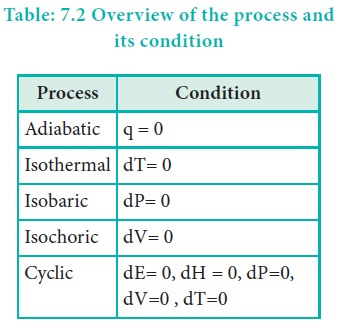
For an adiabatic process q = 0
Isothermal process :
An isothermal process is defined as one in which the temperature of the system remains constant, during the change from its initial to final state. The system exchanges heat with its surrounding and the temperature of the system remains constant. For this purpose the experiment is often performed in a thermostat.
For an isothermal process dT = 0
Isobaric process
An isobaric process is defined as one in which the pressure of the system remains constant during its change from the initial to final state.
For an isobaric process dP= 0 .
Isochoric process
An isochoric process is defined as the one in which the volume of system remains constant during its change from initial to final state. Combustion of a fuel in a bomb calorimeter is an example of an isochoric process.
For an isochoric process, dV= 0.
Cyclic process:
When a system returns to its original state after completing a series of changes, then it is said that a cycle is completed. This process is known as a cyclic process.
For a cyclic process dU = 0, dH = 0, dP=0, dV=0, dT=0
Related Topics