Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipids
Sterols
Sterols
Sterols are compounds containing a cyclic
nucleus namely cyclopentanoperhydro phenanthrene (CPPP) and one or more
hydroxyl groups. They are widely present in animal and plant tissue.
1. Cholesterol
Cholesterol is exclusively found in animals and
is the most abundant animal sterols. It is widely distributed in all cells and
is a major component of cell membrane and lipoproteins. In human beings, it is
very important to control the normal level of cholesterol in blood.
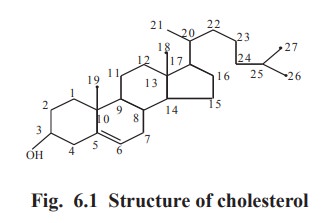
Structure
Cholesterol is a C27(C27H46O)
compound. It has one hydroxyl group at C3 and a double bond between C5 and C6.
An aliphatic side chain is attached to C17. Cholesterol contains a total of 5
methyl groups (Fig. 6.1).
Cholesterol is the precursor of various
physiologically important compounds such as bile acids, vitamin-D, steroid
hormones etc.
Properties
They are white shining rhombic plate like
crystals.
·
It is
tasteless and odourless
·
It has a
high melling point of 150°C.
·
It is
insoluble in water and soluble in fat solvents.
·
It is a
poor conductor of heat and electricity and serves as an insulator against
electric charge. In brain, where it is present abundantly, it acts as an
insulator against nerve impulse which are electrical in nature.
·
Cholesterol,
when oxidised under suitable conditions, undergoes rapid oxidation to form a
ketone-cholestenone.
·
The
hydroxyl group of cholesterol readily forms ester with fatty acids, stearic
acid etc.
·
It gives
addition reactions such as hydrogenation and halogenation because of the
presence of double bond.
Physiological importance of cholesterol
·
It is
one of the essential constituents of cells.
·
It
influences the permeability functions of the cell.
·
It controls
the redcells from being easily hemolyzed.
·
It
performs defensive action.
·
It
assists the formation of bile acids and bile salts, 7- dehydrocholesterol,
vitamin D3, corticosteroid hormones,androgens, estrogens and progesterone.
·
It acts
as an antagonist to phospholipid.
2. Ergosterol
Ergosterol occur in plants. It is also found in
yeast and fungi as the structural constituent of membranes. It is an important
precursor for vitamin-D. When exposed to light, it is converted to
ergocaliciferol, a compound containing vitamin-D activity.
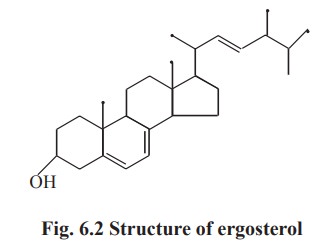
Its structure is similar to that of
cholesterol, but differs in the following aspects.
·
It has
another double bond at C7-C8.
·
It has a
double bond in the side chain.
·
It has
an additional CH3 group in the side chain (Fig 6.2).
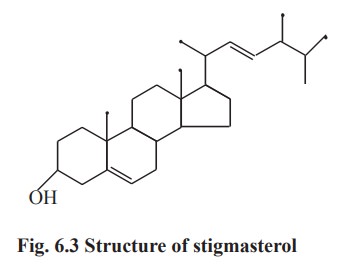
3. Stigma sterol –
It is structurally similar to that of
ergosterol except at C7 (Fig. 6.3) Stigmasterol
and its derivatives sitosterols are probably the mostcommon sterol of plants.
The important sources are soya bean and calabar beans.
Related Topics