Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes
What are fatty acids?
What are fatty acids?
A fatty
acid has a carboxyl group at the polar end and a hydrocarbon chain at the
nonpolar tail. Fatty acids are amphipathic
compounds because the carboxyl group is hydrophilic and the hydrocarbon tail is
hydrophobic. The carboxyl group can ionize under the proper conditions.
A fatty acid that occurs in a living system normally contains an even number of carbon atoms, and the hydrocarbon chain is usually unbranched (Figure 8.1). If there are carbon–carbon double bonds in the chain, the fatty acid is unsaturated; if there are only single bonds, the fatty acid is saturated. Tables 8.1and 8.2 list a few examples of the two classes. In unsaturated fatty acids, the stereochemistry at the double bond is usually cis rather than trans. The differ-ence between cis and trans fatty acids is very important to their overall shape. A cis double bond puts a kink in the long-chain hydrocarbon tail, whereas the shape of a trans fatty acid is like that of a saturated fatty acid in its fully extended conformation. Note that the double bonds are isolated from one another by several singly bonded carbons; fatty acids do not normally have conjugated double-bond systems.
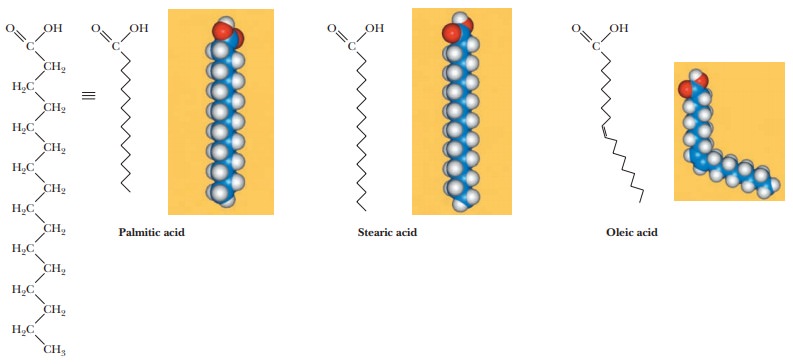
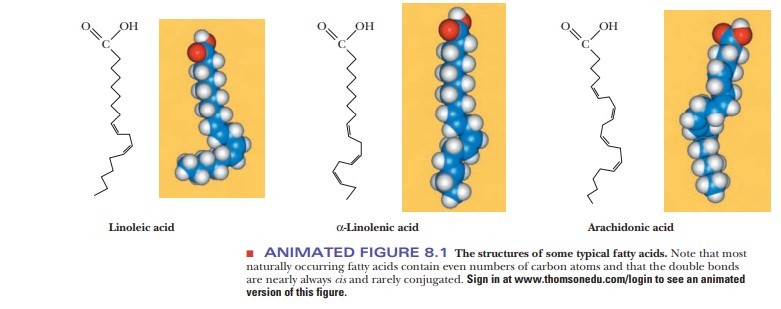
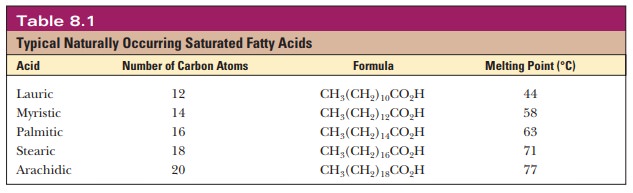
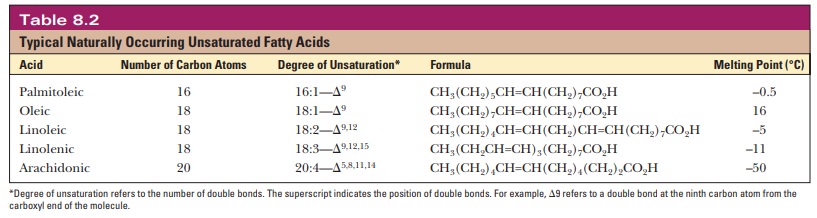
The notation used for fatty acids indicates the number of carbon atoms and the number of double bonds. In this system, 18:0 denotes an 18-carbon saturated fatty acid with no double bonds, and 18:1 denotes an 18-carbon fatty acid with one double bond. Note that in the unsaturated fatty acids in Table 8.2 (except arachidonic acid), there is a double bond at the ninth car-bon atom from the carboxyl end. The position of the double bond results from the way unsaturated fatty acids are synthesized in organisms. Unsaturated fatty acids have lower melting points than saturated ones. Plant oils are liquid at room temperature because they have higher proportions of unsaturated fatty acids than do animal fats, which tend to be solids. Conversion of oils to fats is a commercially important process. It involves hydrogenation, the process of adding hydrogen across the double bond of unsaturated fatty acids to produce the saturated counterpart. Oleomargarine, in particular, uses partially hydrogenated vegetable oils, which tend to include trans fatty acids.
Fatty
acids are rarely found free in nature, but they form parts of many com-monly
occurring lipids.
Related Topics