Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes
How does the composition of the bilayer affect its properties?
How does the composition of the
bilayer affect its properties?
The
arrangement of the hydrocarbon interior of the bilayer can be ordered and rigid
or disordered and fluid. The bilayer’s fluidity depends on its composition. In
saturated fatty acids, a linear arrangement of the hydrocarbon chains leads to
close packing of the molecules in the bilayer, and thus to rigidity.
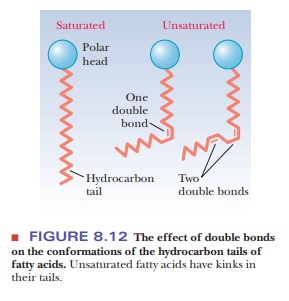
Unsaturated fatty acids have a kink in the hydrocarbon chain that does not
exist in saturated fatty acids (Figure 8.12). The kinks cause disorder in the
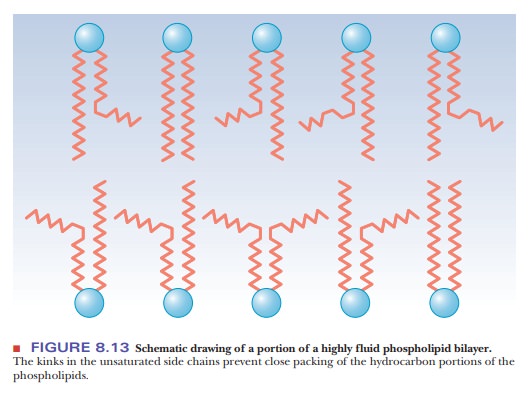
packing of the chains, which makes for a more open structure than would be
possible for straight saturated chains (Figure 8.13). In turn, the disordered
structure caused by the presence of unsaturated fatty acids with cis double bonds (and therefore kinks)
in their hydrocarbon chains causes greater fluidity in the bilayer. The lipid
components of a bilayer are always in motion, to a greater extent in more fluid
bilayers and to a lesser extent in more rigid ones.
The
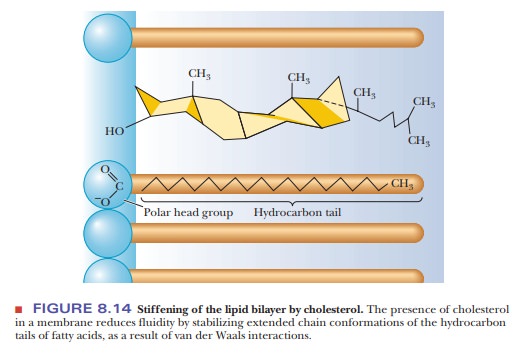
presence of cholesterol may also enhance order and rigidity. The fused-ring
structure of cholesterol is itself quite rigid, and the presence of cholesterol
stabilizes the extended straight-chain arrangement of saturated fatty acids by
van der Waals interactions (Figure 8.14). The lipid portion of a plant membrane
has a higher percentage of unsaturated fatty acids, especially polyunsaturated
(containing two or more double bonds) fatty acids, than does the lipid portion
of an animal membrane. Furthermore, the presence of cho-lesterol is
characteristic of animal, rather than plant, membranes. As a result, animal
membranes are less fluid (more rigid) than plant membranes, and the membranes
of prokaryotes, which contain no appreciable amounts of steroids, are the most
fluid of all. Research suggests that plant sterols can act as natural
cholesterol blockers, interfering with the uptake of dietary cholesterol.
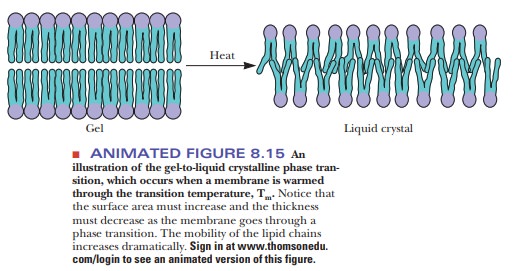
With heat, ordered bilayers become less ordered; bilayers that are compara-tively disordered become even more disordered. This cooperative transition takes place at a characteristic temperature, like the melting of a crystal, which is also a cooperative transition (Figure 8.15).
The transition temperature is higher
for more rigid and ordered membranes than it is for relatively fluid and
disordered membranes. The following Biochemical Connections box looks at some
connections between the fatty acid composition of bilayers and mem-branes and
how they behave at different temperatures.
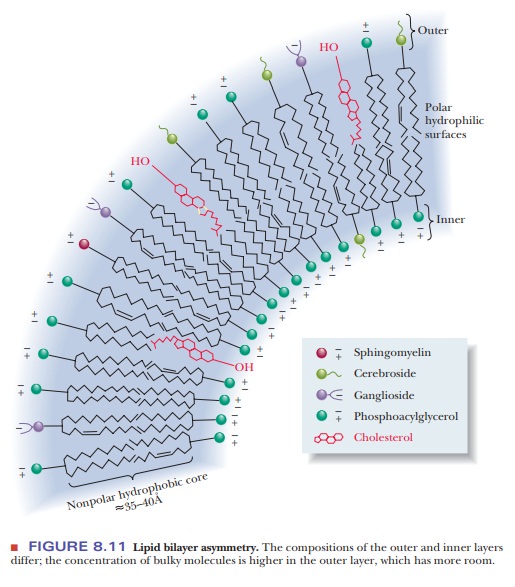
Recall
that the distribution of lipids is not the same in the inner and outer portions
of the bilayer. Because the bilayer is curved, the molecules of the inner layer
are more tightly packed (refer to Figure 8.11). Bulkier molecules, such as
cerebrosides, tend to be located in the outer layer. There is very little
tendency for “flip-flop” migration of lipid molecules from one layer of the
bilayer to another, but it does occur occasionally. Lateral motion of lipid
molecules within one of the two layers frequently takes place, however,
especially in more fluid bilayers. Several methods exist for monitoring the
motions of molecules within a lipid bilayer. These methods depend on label-ing
some part of the lipid component with an easily detected “tag.” The tags are
usually fluorescent compounds, which can be detected with highly sensitive
equipment. Another kind of labeling method depends on the fact that some
nitrogen compounds have unpaired electrons. These compounds are used as labels
and can be detected by magnetic measurements.
Related Topics