Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipids and Proteins Are Associated in Biological Membranes
What are glycolipids?
What are glycolipids?
If a
carbohydrate is bound to an alcohol group of a lipid by a glycosidic linkage,
the resulting compound is a glycolipid.
Quite frequently, ceramides (see
Figure 8.6) are the parent compounds for glycolipids, and the glycosidic bond
is formed between the primary alcohol group of the ceramide and a sugar
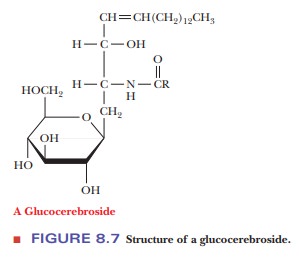
residue. The resulting compound is called a cerebroside. In most cases, the sugar is glucose or galactose; for
example, a glucocerebroside is a cerebroside that contains glucose (Figure
8.7). As the name indicates, cerebrosides are found in nerve and brain cells,
primarily in cell membranes. The carbohydrate portion of these compounds can be
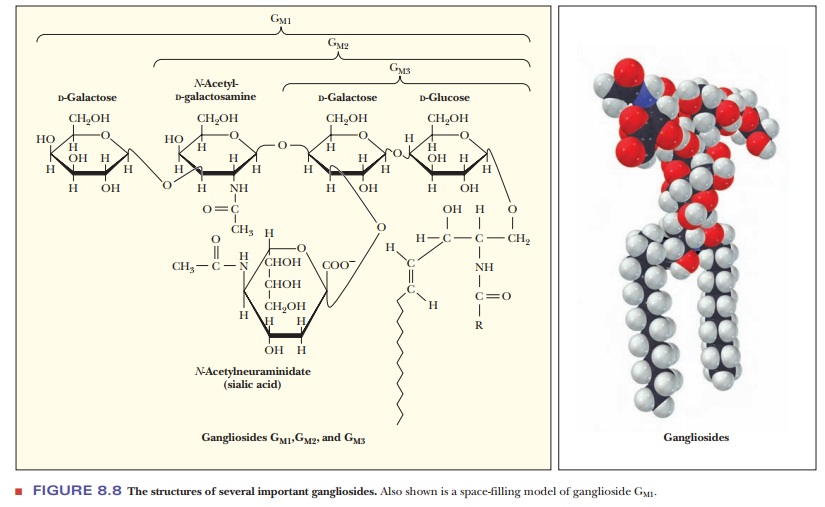
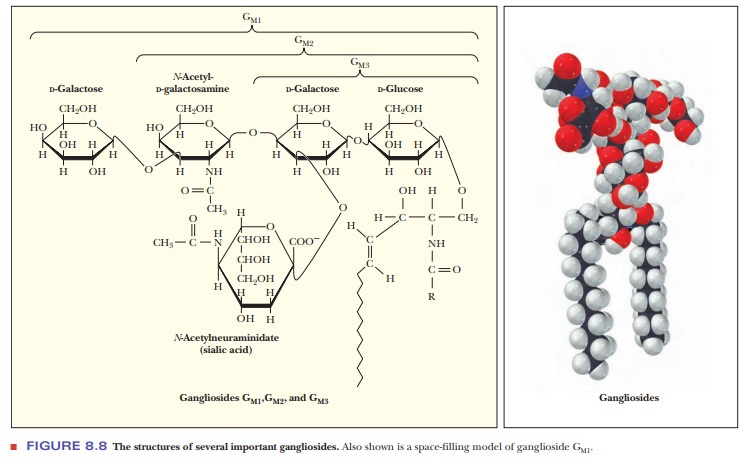
very complex. Gangliosides are examples of glycolipids with a complex
carbohydrate moiety that contains more than three sugars. One of them is always
a sialic acid (Figure 8.8). These compounds are also referred to as acidic
glycosphingolipids because of their net negative charge at neutral pH.
Glycolipids are often found as markers on cell membranes and play a large role
in tissue and organ specificity. Gangliosides are also present in large
quantities in nerve tissues.
Related Topics