Chapter: Biochemistry: Lipids
Classification of Fatty acids
Fatty acids
Fatty acids are carboxylic acid with
hydrocarbon side chains. They are the simplest form of lipids and they are
water soluble. They exist in the body either as free acids or fatty acyl esters
such as triacylglycerol. The fatty acids are released from these lipids on
hydrolysis by lipases.
Classification
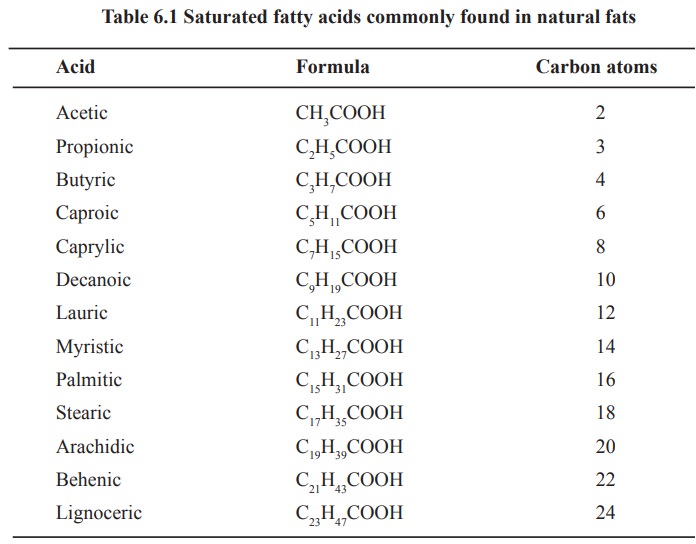
Fatty acids may be divided into (i) saturated
fatty acids and (2) unsaturated fatty acids.
1. Saturated fatty acids
These are fatty acids which donot contain
double bonds. They have general formula CnH2n+1 COOH
(Table 6.1).
2. Unsaturated fatty acid
These are fatty acids which contain double
bonds. They have general formula (CnH2n-1 COOH). They are
subdivided into
a) Monounsaturated fatty acid : These are fatty
acids containing one double bond. (eg) Oleic acid.
CH3 (CH2)7CH =
CH (CH2)7COOH
Oleic acid
2) Polyunsaturated fatty acid : These are fatty
acids that contain more than one double bond.
(eg) linoleic acid, linolenic acid, arachidonic
acid.
Importance
·
They act
as energy stores and fuel molecules.
·
They are
the major components of cell membrane.
3. Essential fatty acid (EFA)
The fatty acids that cannot be synthesised by
the body and therefore should be supplied in the diet are known as essential
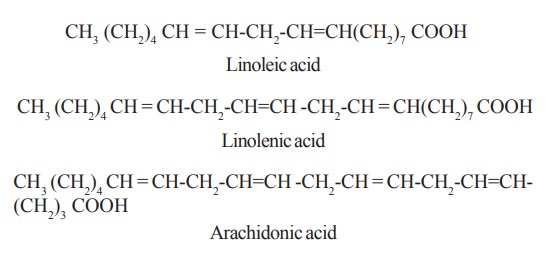
fatty acids. Chemically they are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), namely
linoleic acid, linolenic acid and arachidonic acid.
Structure
CH3 (CH2)4 CH
= CH-CH2-CH=CH(CH2)7 COOH
Linoleic acid
CH3 (CH2)4 CH
= CH-CH2-CH=CH -CH2-CH = CH(CH2)7
COOH
Linolenic acid
CH3 (CH2)4 CH
= CH-CH2-CH=CH -CH2-CH = CH-CH2-CH=CH-(CH2)3
COOH
Arachidonic acid
Functions
·
EFAs are
requried for the membrane structure and functions.They are necessary for the
maintenance of growth, reproduction and good health.
·
They are
important for the transport of cholesterol, formation of lipoportein and
prevention of fatty liver.
·
They
serve as precursor for prostaglandin biosynthesis.
·
They
prolong clotting time and increase fibrinolytic activity.
Related Topics