Algebra | Mathematics - Points to Remember | 10th Mathematics : UNIT 3 : Algebra
Chapter: 10th Mathematics : UNIT 3 : Algebra
Points to Remember
Points to Remember
·
A system of linear equations in three variables will be according
to one of the following cases.
(i) Unique solution
(ii) Infinitely many solutions
(iii) No solution
·
The least common multiple of two or more algebraic expressions is
the expression of lowest degree (or
power) such that the expressions exactly divides it.
·
A polynomial of degree two in variable x is called a quadratic
polynomial in x. Every quadratic polynomial can
have atmost two zeroes. Also the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial intersects
the x-axis
·
The roots of
the quadratic equation ax 2 + bx +c
= 0 , (a ≠ 0) are
given by 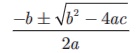
·
For a quadratic equation ax 2 + bx +c
≠ 0
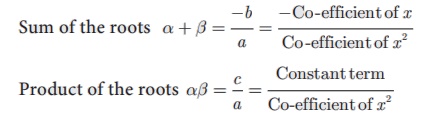
·
If the roots of a quadratic equation are α and β , then the equation is
given by x 2 − (α +
β)x + αβ =0 .
·
The value of the discriminant ( Δ = b 2 − 4ac) decides the nature
of roots as follows
(i) When Δ > 0 , the roots are real and unequal.
(ii) When Δ = 0 , the roots are real and equal.
(iii) When Δ < 0 , there are no real roots.
·
Solving quadratic equation graphically.
·
A matrix is a rectangular array of elements arranged in rows and columns.
·
Order of a matrix
If a matrix A has m number of rows and n
number of columns, then the order of the matrix A is (Number of rows)×(Number
of columns) that is, m ×n .We read m ×n as m
cross n or m by n. It may be noted that m ×n
is not a product of m and n.
·
Types of matrices
(i) A matrix is said to be a row matrix if it has only one row and any number of
columns. A row
matrix is also called as a row vector.
(ii)
A matrix is said to be a column matrix if it has
only one column and any number of rows. It is also called as a column vector.
(iii) A matrix in which the number of rows is equal to the number of columns is called a square matrix.
(iv) A square matrix, all of whose elements, except those in the
leading diagonal are zero is called a diagonal matrix.
(v) A diagonal matrix in which all the leading diagonal elements
are same is called a scalar matrix.
(vi) A square matrix in which elements in the leading diagonal are
all “1” and rest are all zero is called an identity matrix (or) unit matrix.
(vii) A matrix is said to be a zero matrix or null matrix if all its elements are zero.
(viii) If A is a matrix, the matrix obtained by
interchanging the rows and columns of A is called its transpose and is
denoted by AT .
(ix) A square matrix in which all the entries above the leading
diagonal are zero is called a lower triangular matrix.
If all the entries below the leading diagonal are zero, then it is
called an upper triangular matrix.
(x) Two matrices A and B are said to be equal if and
only if they have the same order and each element of matrix A is equal
to the corresponding element of matrix B. That is, a ij
= bij for all i, j.
·
The negative of a matrix Am ×n denoted by −Am ×n is the matrix formed by
replacing each element in the
matrix Am ×n with its additive inverse.
·
Addition and subtraction of matrices
Two matrices can be added or subtracted if they have the same
order. To add or subtract two matrices, simply add or subtract the
corresponding elements.
·
Multiplication of matrix by a scalar
We can multiply the elements of the given matrix A by a
non-zero number k to obtain a new matrix kA whose elements are
multiplied by k. The matrix kA is called scalar multiplication of
A.
Thus if A = (aij )m ×n
then , kA = (kaij )m ×n
for all i = 1,2,…,m and for all j = 1,2,…,n.
Related Topics