Chemical bonding - Orbital Overlap | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Orbital Overlap
Orbital
Overlap
When
atoms combines to form a covalent molecule, the atomic orbitals of the
combining atoms overlap to form a covalent bond. The bond pair of electrons
will occupy the overlapped region of the orbitals. Depending upon the nature of
overlap we can classify the covalent bonding between the two atoms as sigma (σ)
and pi (π) bonds.
Sigma and Pi bonds
When
two atomic orbitals overlap linearly along the axis, the resultant bond is
called a sigma (σ) bond. This overlap is also called 'head-on overlap' or 'axial
overlap'. Overlap involves an s orbital (s-s and s-p overlaps) will always
result in a sigma bond as the s orbital is spherical. Overlap between two p
orbitals along the molecular axis will also result in sigma bond formation.
When we consider x-axis as molecular axis, the px-px
overlap will result in σ-bond.
When
two atomic orbitals overlaps sideways, the resultant covalent bond is called a
pi (π)bond. When we consider x-axis as molecular axis, the py-py
and pz-pz overlaps will result in the formation of a
π-bond.
Following
examples will be useful to understand the overlap:
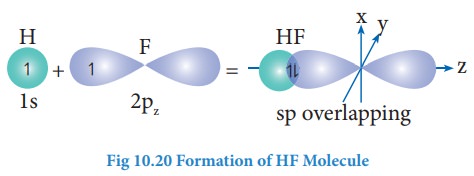
Formation of hydrogen (H2) Molecule
Electronic
configuration of hydrogen atom is 1s1
During
the formation of H2 molecule, the 1s orbitals of two hydrogen atoms
containing one unpaired electron with opposite spin overlap with each other
along the internuclear axis. This overlap is called s-s overlap. Such axial
overlap results in the formation of a σ-covalent bond.
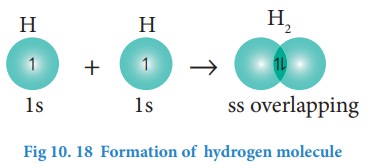
Formation of fluorine molecule (F2):
Valence
shell electronic configuration of fluorine atom : 2s2 2px2,
2py2, 2pz1
When
the half filled pz orbitals of two fluorine overlaps along the
z-axis, a σ-covalent bond is formed between them.
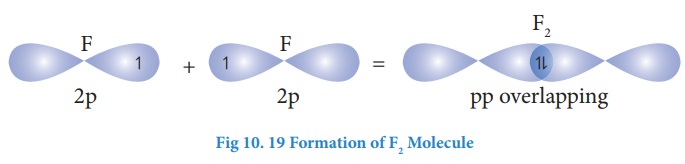
Formation of HF molecule:
Electronic
configuration of hydrogen atom is 1s1
Valence
shell electronic configuration of fluorine atom : 2s2 2px2,
2py2, 2pz1
When
half filled 1s orbital of hydrogen linearly overlaps with a half filled 2pz
orbital of fluorine, a σ-covalent bond is formed between hydrogen and fluorine.
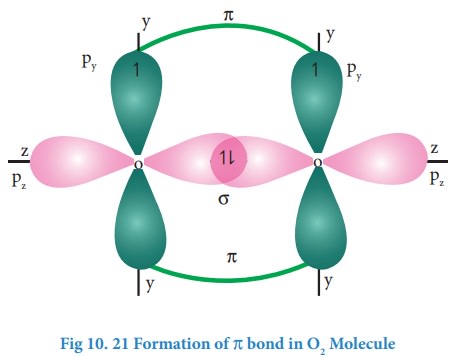
Formation of oxygen molecule (O2):
Valence
shell electronic configuration of oxygen atom : 2s2 2px2,
2py1, 2pz1
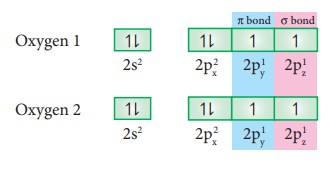
When
the half filled pz orbitals of two oxygen overlaps along the z-axis
(considering molecular axis as z axis), a σ-covalent bond is formed between
them. Other two half filled py orbitals of two oxygen atoms overlap
laterally (sideways) to form a π-covalent bond between the oxygen atoms. Thus,
in oxygen molecule, two oxygen atoms are connected by two covalent bonds
(double bond). The other two pair of electrons present in the 2s and 2px
orbital do not involve in bonding and remains as lone pairs on the respective
oxygen.
Related Topics