Chemical bonding - Bond order | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Bond order
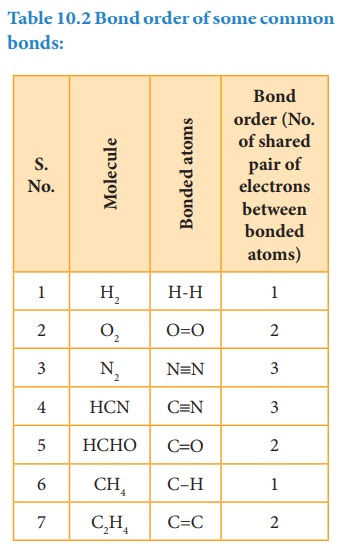
The number of bonds formed between the two bonded atoms in a molecule is called the bond order.
Bond order
The number of bonds formed between the two bonded atoms in a molecule is called the bond order. In Lewis theory, the bond order is equal to the number of shared pair of electrons between the two bonded atoms. For example in hydrogen molecules, there is only one shared pair of electrons and hence, the bond order is one. Similarly, in H2O, HCl, Methane, etc the central atom forms single bonds with bond order of one.
Tags : Chemical bonding , 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Study Material, Lecturing Notes, Assignment, Reference, Wiki description explanation, brief detail
11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding : Bond order | Chemical bonding
Related Topics
11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding