Chemical bonding | Chemistry - Coordinate covalent bond | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Coordinate covalent bond
Coordinate
covalent bond
In
the formation of a covalent bond, both the combining atoms contribute one
electron each and the these electrons are mutually shared among them. However,
in certain bond formation, one of the combining atoms donates a pair of
electrons i.e. two electrons which are necessary for the covalent bond
formation, and these electrons are shared by both the combining atoms.
These
type of bonds are called coordinate covalent bond or coordinate bond. The
combining atom which donates the pair of electron is called a donor atom and
the other atom an acceptor atom. This bond is denoted by an arrow starting from
the donor atom pointing towards the acceptor atom. (Later in coordination
compound, we will refer the donor atom as ligand and the acceptor atom as
central-metal atom/ion.
![]()
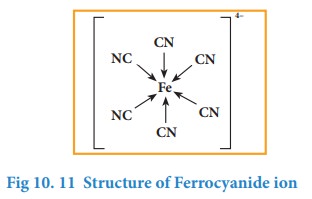
![]() For Example, in ferrocynide ion [Fe(CN)6]4–,
each cyanide ion (CN–) donates a pair of electrons to form a
coordinate bond with iron (Fe2+) and these electrons are shared by
Fe2+ and CN-.
For Example, in ferrocynide ion [Fe(CN)6]4–,
each cyanide ion (CN–) donates a pair of electrons to form a
coordinate bond with iron (Fe2+) and these electrons are shared by
Fe2+ and CN-.
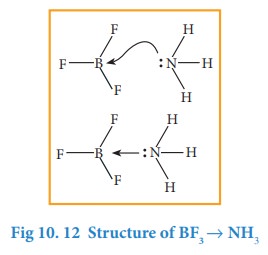
In
certain cases, molecules having a lone pair of electrons such as ammonia
donates its pair to an electron deficient molecules such as BF3. to
form a coordinate
Related Topics