Chemical bonding - Bond length | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Chemical bonding
Bond length
Bond length
The distance between the nuclei of the two covalently bonded atoms is called bond length. Consider a covalent molecule A-B. The bond length is given by the sum of the radii of the bonded atoms (rA + rB). The length of a bond can be determined by spectroscopic, x-ray diffraction and electron-diffraction techniques The bond length depends on the size of the atom and the number of bonds (multiplicity) between the combining atoms.
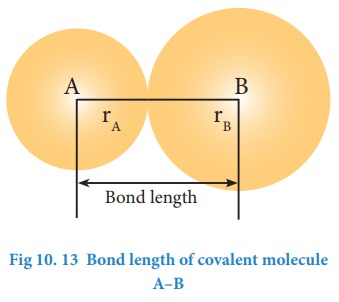
Greater the size of the atom, greater will be the bond length. For example, carbon-carbon single bond length (1.54 Å) is longer than the carbon-nitrogen single bond length (1.43 Å).
Increase in the number of bonds between the two atoms decreases the bond length. For example, the carbon-carbon single bond is longer than the carbon-carbon double bond (1.33 Å) and the carbon-carbon triple bond (1.20 Å).
![]()
![]()
Related Topics